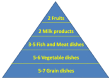
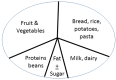
Inclusion of fermented foods in food guides around the world
- PMID: 25580813
- PMCID: PMC4303846
- DOI: 10.3390/nu7010390
Inclusion of fermented foods in food guides around the world
Abstract
Fermented foods have been a well-established part of the human diet for thousands of years, without much of an appreciation for, or an understanding of, their underlying microbial functionality, until recently. The use of many organisms derived from these foods, and their applications in probiotics, have further illustrated their impact on gastrointestinal wellbeing and diseases affecting other sites in the body. However, despite the many benefits of fermented foods, their recommended consumption has not been widely translated to global inclusion in food guides. Here, we present the case for such inclusion, and challenge health authorities around the world to consider advocating for the many benefits of these foods.
Figures
References
-
- Various A. Regimen for Health. In: Lloyd G.E.R., Chadwick J., Mann W.N., editors. Hippocratic Writings. Penguin Books Ltd.; London, UK: 1983. pp. 154–196.
-
- Canada’s Food Guides from 1942 to 1992. [(accessed on 12 October 2014)]. Available online: http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/fn-an/food-guide-aliment/context/fg_history-histo....
-
- Walker P.M.B. Chambers Science and Technology Dictionary. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1988.
-
- Health and Nutritional Properties of Probiotics in Food Including Powder Milk with Live Lactic Acid Bacteria. [(accessed on 23 September 2014)]. Available online: ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/009/a0512e/a0512e00.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources