A rapid enzymatic assay for high-throughput screening of adenosine-producing strains
- PMID: 25580842
- PMCID: PMC4353337
- DOI: 10.1111/1751-7915.12189
A rapid enzymatic assay for high-throughput screening of adenosine-producing strains
Abstract
Adenosine is a major local regulator of tissue function and industrially useful as precursor for the production of medicinal nucleoside substances. High-throughput screening of adenosine overproducers is important for industrial microorganism breeding. An enzymatic assay of adenosine was developed by combined adenosine deaminase (ADA) with indophenol method. The ADA catalyzes the cleavage of adenosine to inosine and NH3 , the latter can be accurately determined by indophenol method. The assay system was optimized to deliver a good performance and could tolerate the addition of inorganic salts and many nutrition components to the assay mixtures. Adenosine could be accurately determined by this assay using 96-well microplates. Spike and recovery tests showed that this assay can accurately and reproducibly determine increases in adenosine in fermentation broth without any pretreatment to remove proteins and potentially interfering low-molecular-weight molecules. This assay was also applied to high-throughput screening for high adenosine-producing strains. The high selectivity and accuracy of the ADA assay provides rapid and high-throughput analysis of adenosine in large numbers of samples.
© 2014 The Authors. Microbial Biotechnology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Society for Applied Microbiology.
Figures
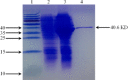


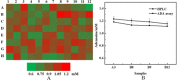

References
-
- Asada M, Yanamoto K, Nakanishi K, Matsuno R, Kirnura A. Kamikubo T. Long term continuous ATP regeneration by enzymes of the alcohol fermentation pathway and kinases of yeast. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1981;12:198–204.
-
- Chen X, Zhang C, Cheng J, Shi X, Li L, Zhang Z, et al. Enhancement of adenosine production by Bacillus subtilis CGMCC 4484 through metabolic flux analysis and simplified feeding strategies. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2013;36:1851–1859. - PubMed
-
- Diaz J, Tornel PL. Martinez P. Reference intervals for blood ammonia in healthy subjects, determined by microdiffusion. Clin Chem. 1995;41:1048. - PubMed
-
- Dienst SG. An ion exchange method for plasma ammonia concentration. J Lab Clin Med. 1961;58:149–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

