Extreme oncoplasty: breast conservation for patients who need mastectomy
- PMID: 25583035
- PMCID: PMC4303932
- DOI: 10.1111/tbj.12356
Extreme oncoplasty: breast conservation for patients who need mastectomy
Abstract
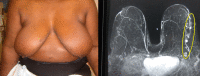
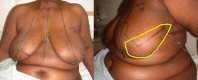
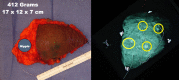
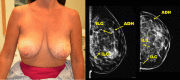
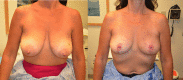
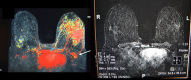
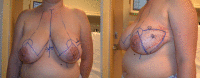
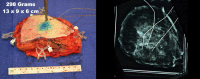
Extreme oncoplasty is a breast conserving operation, using oncoplastic techniques, in a patient who, in most physicians' opinions, requires a mastectomy. These are generally large, greater than 5 cm multifocal or multicentric tumors. Many will have positive lymph nodes. Most will require radiation therapy, even if treated with mastectomy. Sixty-six consecutive patients with multifocal, multicentric, or locally advanced tumors that spanned more than 50 mm were studied (extreme cases). All patients underwent excision and oncoplastic reconstruction using a standard or split wise pattern reduction and immediate contralateral surgery for symmetry. All received postexcisional standard whole breast radiation therapy with a boost to the tumor bed. The extreme cases were compared with 245 consecutive patients with unifocal or multifocal tumors that spanned 50 mm or less (standard cases). All extreme patients were advised to have a mastectomy; all sought a breast conserving second opinion. Diagnostic evaluation included digital mammography, ultrasound, MRI, and PET-CT (if invasive). Standard cases did extremely well. No ink on tumor was achieved 96% of the time among 245 patients. The median tumor size was 21 mm (mean 23 mm). Margins equal or greater than 1 mm were achieved in 88.6% of patients. Seventeen (6.9%) standard patients underwent re-excision to achieve wider margins and only one patient (0.4%) was converted to mastectomy. With 24 months of median follow-up, three patients (1.2%) experienced local recurrence. For extreme cases, no ink on tumor was achieved 83.3% of the time, which is comparable to published positive margin rates after standard lumpectomy. The median tumor size was 62 mm (mean 77 mm). Margins equal or greater than 1 mm were achieved in 54.5% of patients. Six (9.1%) extreme patients underwent re-excision to achieve wider margins and four patients (6.1%) were converted to mastectomy. With a follow-up of 24 months, one patient (1.5%) experienced a local recurrence. Extreme oncoplasty is a promising new concept. It allows successful breast conservation in selected patients with greater than 5 cm multifocal/multicentric tumors. It may be useful in patients with locally advanced tumors following neo-adjuvant chemotherapy. From a quality of life point of view, it is a better option than the combination of mastectomy, reconstruction, and radiation therapy. Long-term data on recurrence and survival are not available, using this approach. Based on historical data, it is expected the local recurrence will be somewhat higher but that there will be little or no impact on survival.
Keywords: avoiding mastectomy; breast conservation for large tumors; extreme oncoplasty; multifocal/multicentric breast tumors; oncoplastic breast conservation.
© 2015 The Authors The Breast Journal Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




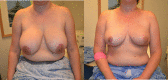
References
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Bryant J, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing total mastectomy, lumpectomy, and lumpectomy plus irradiation for the treatment of invasive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1233–41. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Bauer M, Margolese R, et al. Five-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing total mastectomy and lumpectomy with or without radiation therapy in the treatment of breast cancer. N Eng J Med. 1985;312:665–73. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L, et al. Twenty-year follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1227–32. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Saccozzi R, Del Vecchio M, et al. Comparing radical mastectomy with quadrantectomy, axillary dissection and radiotherapy in patients with small cancers of the breast. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:6–10. - PubMed
-
- Lichter A, Lippman M, Danforth D, et al. Mastectomy versus breast conserving therapy in the treatment of stage I and II carcinoma of the breast: a randomized trial at The National Cancer Institute. J Clin Oncol. 1992;10:976–82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

