Impaired Hippo signaling promotes Rho1-JNK-dependent growth
- PMID: 25583514
- PMCID: PMC4313816
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1415020112
Impaired Hippo signaling promotes Rho1-JNK-dependent growth
Abstract
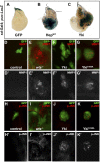
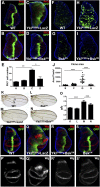
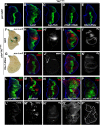
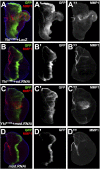
The Hippo and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway both regulate growth and contribute to tumorigenesis when dysregulated. Whereas the Hippo pathway acts via the transcription coactivator Yki/YAP to regulate target gene expression, JNK signaling, triggered by various modulators including Rho GTPases, activates the transcription factors Jun and Fos. Here, we show that impaired Hippo signaling induces JNK activation through Rho1. Blocking Rho1-JNK signaling suppresses Yki-induced overgrowth in the wing disk, whereas ectopic Rho1 expression promotes tissue growth when apoptosis is prohibited. Furthermore, Yki directly regulates Rho1 transcription via the transcription factor Sd. Thus, our results have identified a novel molecular link between the Hippo and JNK pathways and implicated the essential role of the JNK pathway in Hippo signaling-related tumorigenesis.
Keywords: Drosophila; Hippo; JNK; Rho1; growth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. - PubMed
-
- Harvey KF, Zhang X, Thomas DM. The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13(4):246–257. - PubMed
-
- Huang J, Wu S, Barrera J, Matthews K, Pan D. The Hippo signaling pathway coordinately regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila homolog of YAP. Cell. 2005;122(3):421–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

