A small molecule, odanacatib, inhibits inflammation and bone loss caused by endodontic disease
- PMID: 25583522
- PMCID: PMC4363442
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01713-14
A small molecule, odanacatib, inhibits inflammation and bone loss caused by endodontic disease
Abstract
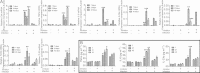
Periapical disease, an inflammatory disease mainly caused by dental caries, is one of the most prevalent infectious diseases of humans, affecting both children and adults. The infection travels through the root, leading to inflammation, bone destruction, and severe pain for the patient. Therefore, the development of a new class of anti-periapical disease therapies is necessary and critical for treatment and prevention. A small molecule, odanacatib (ODN), which is a cathepsin K (Ctsk) inhibitor, was investigated to determine its ability to treat this disease in a mouse model of periapical disease. While Ctsk was originally found in osteoclasts as an osteoclast-specific lysosomal protease, we were surprised to find that ODN can suppress the bacterium-induced immune response as well as bone destruction in the lesion area. X rays and microcomputed tomography (micro-CT) showed that ODN treatment had significant bone protection effects at different time points. Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescent staining show that ODN treatment dramatically decreased F4/80+ macrophages and CD3+ T cells in the lesion areas 42 days after infection. Consistent with these findings, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) analysis showed low levels of proinflammatory mRNAs (for tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 6, and interleukin 23α) and corresponding cytokine expression in the ODN-treated disease group. The levels of mRNA for Toll-like receptors 4, 5, and 9 also largely decreased in the ODN-treated disease group. Our results demonstrated that ODN can inhibit endodontic disease development, bone erosion, and immune response. These results indicate that application of this small molecule offers a new opportunity to design effective therapies that could prevent periapical inflammation and revolutionize current treatment options.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
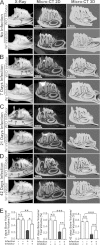
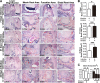

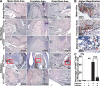
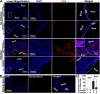

References
-
- Jiang H, Chen W, Zhu G, Zhang L, Tucker B, Hao L, Feng S, Ci H, Ma J, Wang L, Stashenko P, Li YP. 2013. RNAi-mediated silencing of Atp6i and Atp6i haploinsufficiency prevents both bone loss and inflammation in a mouse model of periodontal disease. PLoS One 8:e58599. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058599. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang S, Hao L, McConnell M, Zhou X, Wang M, Zhang Y, Mountz JD, Reddy M, Eleazer PD, Li YP, Chen W. 2013. Inhibition of Rgs10 expression prevents immune cell infiltration in bacteria-induced inflammatory lesions and osteoclast-mediated bone destruction. Bone Res 1:267–281. doi:10.4248/BR201303005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

