Mycobacterium tuberculosis gyrase inhibitors as a new class of antitubercular drugs
- PMID: 25583730
- PMCID: PMC4356839
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.03913-14
Mycobacterium tuberculosis gyrase inhibitors as a new class of antitubercular drugs
Abstract
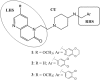
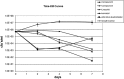
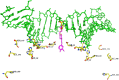
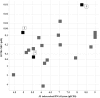
One way to speed up the TB drug discovery process is to search for antitubercular activity among compound series that already possess some of the key properties needed in anti-infective drug discovery, such as whole-cell activity and oral absorption. Here, we present MGIs, a new series of Mycobacterium tuberculosis gyrase inhibitors, which stem from the long-term efforts GSK has dedicated to the discovery and development of novel bacterial topoisomerase inhibitors (NBTIs). The compounds identified were found to be devoid of fluoroquinolone (FQ) cross-resistance and seem to operate through a mechanism similar to that of the previously described NBTI GSK antibacterial drug candidate. The remarkable in vitro and in vivo antitubercular profiles showed by the hits has prompted us to further advance the MGI project to full lead optimization.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
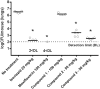
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2012. Global tuberculosis report 2012. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- World Health Organization. 2013. Global tuberculosis report 2013. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- World Health Organization. 2006. The stop TB strategy. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland: http://www.who.int/tb/strategy/en/.
-
- World Health Organization. 2009. Treatment of tuberculosis: guidelines for national programs, 4th ed WHO/HTM/TB/2009.420 World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- World Health Organization. 2010. Multidrug and extensively drug-resistant TB (M/XDR-TB): 2010 global report on surveillance and response. WHO/HTM/TB/2010.3 World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

