Neonatal treatment of CINCA syndrome
- PMID: 25584041
- PMCID: PMC4290099
- DOI: 10.1186/1546-0096-12-52
Neonatal treatment of CINCA syndrome
Abstract
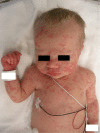
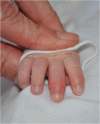
Chronic Infantile Neurological Cutaneous Articular (CINCA) syndrome, also called Neonatal Onset Multisystem Inflammatory Disease (NOMID) is a chronic disease with early onset affecting mainly the central nervous system, bones and joints and may lead to permanent damage. We report two preterm infants with severe CINCA syndrome treated by anti-interleukin-1 in the neonatal period, although, so far, no experience with this treatment in infants younger than three months of age has been reported. A review of the literature was performed with focus on treatment and neonatal features of CINCA syndrome.
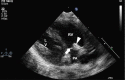
Case report: Two cases suspected to have CINCA syndrome were put on treatment with anakinra in the early neonatal period due to severe clinical presentation. We observed a rapid and persistent decline of clinical signs and systemic inflammation and good drug tolerance. Diagnosis was confirmed in both cases by mutations in the NLRP3/CIAS1-gene coding for cryopyrin. As particular neonatal clinical signs polyhydramnios and endocardial overgrowth are to be mentioned.
Conclusion: We strongly suggest that specific treatment targeting interleukin-1 activity should be started early. Being well tolerated, it can be introduced already in neonates presenting clinical signs of severe CINCA syndrome in order to rapidly control inflammation and to prevent life-long disability.
Keywords: Anakinra; CINCA; IL-1 receptor; IL-1β; NOMID; Neonatal treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Kuemmerle-Deschner JB, Tyrrell PN, Koetter I, Wittkowski H, Bialkowski A, Tzaribachev N, Lohse P, Koitchev A, Deuter C, Foell D, Benseler SM. Efficacy and safety of anakinra therapy in pediatric and adult patients with the autoinflammatory Muckle-Wells syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:840–849. doi: 10.1002/art.30149. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sibley CH, Plass N, Snow J, Wiggs EA, Brewer CC, King KA, Zalewski C, Kim HJ, Bishop R, Hill S, Paul SM, Kicker P, Phillips Z, Dolan JG, Widemann B, Jayaprakash N, Pucino F, Stone DL, Chapelle D, Snyder C, Butman JA, Wesley R, Goldbach-Mansky R. Sustained response and prevention of damage progression in patients with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease treated with anakinra: a cohort study to determine three- and five-year outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:2375–2386. doi: 10.1002/art.34409. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Neven B, Marvillet I, Terrada C, Ferster A, Boddaert N, Couloignier V, Pinto G, Pagnier A, Bodemer C, Bodaghi B, Tardieu M, Prieur AM, Quartier P. Long-term efficacy of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist anakinra in ten patients with neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease/chronic infantile neurologic, cutaneous, articular syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:258–267. doi: 10.1002/art.25057. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

