Bile acids as metabolic regulators
- PMID: 25584736
- PMCID: PMC4332523
- DOI: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000156
Bile acids as metabolic regulators
Abstract
Purpose of review: This review focuses on the latest understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the complex interactions between intestine and liver bile acid signaling, gut microbiota, and their impact on whole-body lipid, glucose and energy metabolism.
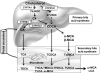
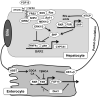
Recent findings: Hepatic bile acid synthesis is tightly regulated by the bile acid negative feedback mechanisms. Modulating the enterohepatic bile acid signaling greatly impacts the whole-body metabolic homeostasis. Recently, a positive feedback mechanism through intestine farnesoid X receptor (FXR) antagonism has been proposed to link gut microbiota to the regulation of bile acid composition and pool size. Two studies identified intestine Diet1 and hepatic SHP-2 as novel regulators of CYP7A1 and bile acid synthesis through the gut-liver FXR-fibroblast growth factor 15/19-FGF receptor four signaling axis. New evidence suggests that enhancing bile acid signaling in the distal ileum and colon contributes to the metabolic benefits of bile acid sequestrants and bariatric surgery.
Summary: Small-molecule ligands that target TGR5 and FXR have shown promise in treating various metabolic and inflammation-related human diseases. New insights into the mechanisms underlying the bariatric surgery and bile acid sequestrant treatment suggest that targeting the enterohepatic circulation to modulate gut-liver bile acid signaling, incretin production and microbiota represents a new strategy to treat obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Chiang JY. Bile acid regulation of gene expression: roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr Rev. 2002;23:443–463. - PubMed
-
- Lu TT, Makishima M, Repa JJ, Schoonjans K, Kerr TA, Auwerx J, Mangelsdorf DJ. Molecular basis for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol Cell. 2000;6:507–515. - PubMed
-
- Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, Watson MA, McKee DD, Moore LB, Galardi C, Wilson JG, Lewis MC, Roth ME, Maloney PR, Willson TM, Kliewer SA. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell. 2000;6:517–526. - PubMed
-
- Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA, Gerard RD, Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA. Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2005;2:217–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK44442/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK102487/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK044442/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK102487-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5P20RR021940-07/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK058379/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR021940/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK058379/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 8 P20 GM103549-07/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK58379/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044442/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103549/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

