Isolation and biochemical characterization of Apios tuber lectin
- PMID: 25584830
- PMCID: PMC6272198
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules20010987
Isolation and biochemical characterization of Apios tuber lectin
Abstract
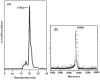
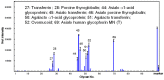
Apios tuber lectin, named ATL, was isolated from Apios americana Medikus by two chromatography steps, hydrophobic chromatography and anion-exchange chromatography. The minimum concentration required for the hemagglutination activity toward rabbit erythrocytes of ATL was 4 μg/mL. ATL was composed of a homodimer of 28.4 kDa subunits. The amino acid sequence of ATL was similar to those of other legume lectins. The lectin showed moderate stability toward heating and acidic pH, and the binding affinity against several monosaccharides, such as D-glucosamine and D-galactosamine. ATL also bound to desialylated or agalactosylated glycoproteins such as asialo and agalacto transferrin. ATL decreased the transepithelial electrical resistance across human intestinal Caco-2 cell monolayers, suggesting the effect on the tight junction-mediated paracellular transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Sharon N., Lis H. Lectins. 2nd ed. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2003. Detection, occurrence and isolation; pp. 33–61.
-
- Van Damme E.J.M., Peumans W.J., Pusztai A., Bardoez S. Lectin classification. In: van Damme E.J.M., Peumans W.J., Pusztai A., Bardoez S., editors. Handbook of Plant Lectins: Properties and Biochemical Applications. John Wiley & Sons; West Sussex, UK: 1998. pp. 31–55.
-
- Van Damme E.J.M., Peumans W.J., Barre A., Rougé P. Plant lectins: A composite of several distinct families of structurally and evolutionary related proteins with diverse biological roles. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1998;17:575–692. doi: 10.1016/S0735-2689(98)00365-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

