Asparaginase pharmacokinetics and implications of therapeutic drug monitoring
- PMID: 25586605
- PMCID: PMC4732456
- DOI: 10.3109/10428194.2014.1003056
Asparaginase pharmacokinetics and implications of therapeutic drug monitoring
Abstract
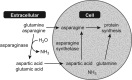
Asparaginase is widely used in chemotherapeutic regimens for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and has led to a substantial improvement in cure rates, especially in children. Optimal therapeutic effects depend on a complete and sustained depletion of serum asparagine. However, pronounced interpatient variability, differences in pharmacokinetic properties between asparaginases and the formation of asparaginase antibodies make it difficult to predict the degree of asparagine depletion that will result from a given dose of asparaginase. The pharmacological principles underlying asparaginase therapy in the treatment of ALL are summarized in this article. A better understanding of the many factors that influence asparaginase activity and subsequent asparagine depletion may allow physicians to tailor treatment to the individual, maximizing therapeutic effect and minimizing treatment-related toxicity. Therapeutic drug monitoring provides a means of assessing a patient's current depletion status and can be used to better evaluate the potential benefit of treatment adjustments.
Keywords: Asparaginase; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; hypersensitivity; pharmacokinetics; silent inactivation; therapeutic drug monitoring.
Figures
References
-
- Muller HJ, Boos J. Use of L-asparaginase in childhood ALL. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1998;28:97–113. - PubMed
-
- Boos J, Werber G, Ahlke E, et al. Monitoring of asparaginase activity and asparagine levels in children on different asparaginase preparations. Eur J Cancer. 1996;32A:1544–1550. - PubMed
-
- Vieira Pinheiro JP, Ahlke E, Nowak-Gottl U, et al. Pharmacokinetic dose adjustment of Erwinia asparaginase in protocol II of the paediatric ALL/NHL-BFM treatment protocols. Br J Haematol. 1999;104:313–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources