Role of α-synuclein in inducing innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson disease
- PMID: 25588354
- PMCID: PMC4405142
- DOI: 10.3233/JPD-140491
Role of α-synuclein in inducing innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson disease
Abstract
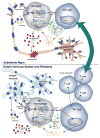
Alpha-synuclein (α-syn) is central to the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease (PD). Gene duplications, triplications and point mutations in SNCA1, the gene encoding α-syn, cause autosomal dominant forms of PD. Aggregated and post-translationally modified forms of α-syn are present in Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in both sporadic and familial PD, and recent work has emphasized the prion-like ability of aggregated α-syn to produce spreading pathology. Accumulation of abnormal forms of α-syn is a trigger for PD, but recent evidence suggests that much of the downstream neurodegeneration may result from inflammatory responses. Components of both the innate and adaptive immune systems are activated in PD, and influencing interactions between innate and adaptive immune components has been shown to modify the pathological process in animal models of PD. Understanding the relationship between α-syn and subsequent inflammation may reveal novel targets for neuroprotective interventions. In this review, we examine the role of α-syn and modified forms of this protein in the initiation of innate and adaptive immune responses.
Keywords: Parkinson disease; T-lymphocyte; adaptive immunity; alpha-synuclein; antigen presentation; innate immunity; microglia; post-translational modifications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures
References
-
- Jakes R, Spillantini MG, Goedert M. Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett. 1994;345:27–32. - PubMed
-
- Giasson BI, Uryu K, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Mutant and wild type human alpha-synucleins assemble into elongated filaments with distinct morphologies in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:7619–7622. - PubMed
-
- Conway KA, Harper JD, Lansbury PT., Jr Fibrils formed in vitro from alpha-synuclein and two mutant forms linked to Parkinson’s disease are typical amyloid. Biochemistry. 2000;39:2552–2563. - PubMed
-
- Perrin RJ, Woods WS, Clayton DF, George JM. Interaction of human alpha-Synuclein and Parkinson’s disease variants with phospholipids. Structural analysis using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:34393–34398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

