Body weight and risk of atrial fibrillation in 7,169 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes; an observational study
- PMID: 25589001
- PMCID: PMC4299152
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-014-0170-3
Body weight and risk of atrial fibrillation in 7,169 patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes; an observational study
Abstract
Background: Obesity, type 2 diabetes and atrial fibrillation (AF) are closely associated, but the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. We aimed to explore associations between body mass index (BMI) or weight change with risk of AF in patients with type 2 diabetes.
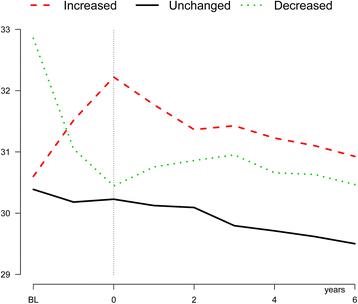
Methods: A total of 7,169 participations with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes were stratified according to baseline BMI, and after a second BMI measurement within 18 months, further grouped according to relative weight change as "weight gain" (>1 BMI unit), "stable weight" (+/- 1 BMI unit) and "weight loss" (<1 BMI unit). The mean follow-up period was 4.6 years, and the risk of AF was estimated using adjusted Cox regression models.
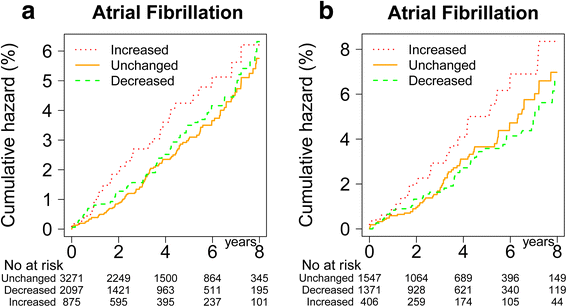
Results: Average age at diabetes diagnosis was 60 years and the patients were slightly obese (mean BMI 30.2 kg/m(2)). During follow-up, 287 patients developed incident AF, and those with overweight or obesity at baseline had 1.9-fold and 2.9-fold higher risk of AF, respectively, than those with normal BMI. The 14% of the patients with subsequent weight gain had 1.5-fold risk of AF compared with those with stable weight or weight loss.
Conclusions: In patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, baseline overweight and obesity, as well as modest weight increase during the first 18 months after diagnosis, were associated with a substantially increased risk of incident AF. Patients with type 2 diabetes may benefit from efforts to prevent weight gain in order to reduce the risk of incident AF.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01121315.
Figures

References
-
- Miyasaka Y, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Cha SS, Bailey KR, Abhayaratna WP, Seward JB, Tsang TS. Secular trends in incidence of atrial fibrillation in Olmsted County, Minnesota, 1980 to 2000, and implications on the projections for future prevalence. Circulation. 2006;114:119–125. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.595140. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Benjamin EJ, Chen PS, Bild DE, Mascette AM, Albert CM, Alonso A, Calkins H, Connolly SJ, Curtis AB, Darbar D, Ellinor PT, Go AS, Goldschlager NF, Heckbert SR, Jalife J, Kerr CR, Levy D, Lloyd-Jones DM, Massie BM, Nattel S, Olgin JE, Packer DL, Po SS, Tsang TS, Van Wagoner DR, Waldo AL, Wyse DG. Prevention of atrial fibrillation: report from a national heart, lung, and blood institute workshop. Circulation. 2009;119:606–618. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.825380. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ryden L, Grant PJ, Anker SD, Berne C, Cosentino F, Danchin N, et al. ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD: The Task Force on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and developed in collaboration with the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Eur Heart J. 2013;34:3035–3087. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht108. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, Lin JK, Farzadfar F, Khang YH, Stevens GA, Rao M, Ali MK, Riley LM, Robinson CA, Ezzati M. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 27 million participants. Lancet. 2011;378:31–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60679-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

