Does Extended Pre Quit Bupropion Aid in Extinguishing Smoking Behavior?
- PMID: 25589680
- PMCID: PMC4612343
- DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntu347
Does Extended Pre Quit Bupropion Aid in Extinguishing Smoking Behavior?
Abstract
Introduction: Understanding the mechanisms by which bupropion promotes smoking cessation may lead to more effective treatment. To the extent that reduced smoking reinforcement is one such mechanism, a longer duration of pre quit bupropion treatment should promote extinction of smoking behavior. We evaluated whether 4 weeks of pre quit bupropion (extended run-in) results in greater pre quit reductions in smoking rate and cotinine and, secondarily, greater short-term abstinence, than standard 1 week of pre quit bupropion (standard run-in).
Methods: Adult smokers (n = 95; 48 females) were randomized to a standard run-in group (n = 48; 3-week placebo, then 1-week bupropion pre quit) or an extended run-in group (4-week pre quit bupropion; n = 47). Both groups received group behavioral counseling and 7 weeks of post quit bupropion. Smoking rate (and craving, withdrawal, and subjective effects) was collected daily during the pre quit period; biochemical data (cotinine and carbon monoxide) were collected at study visits.
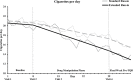
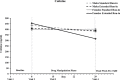
Results: During the pre quit period, the extended run-in group exhibited a greater decrease in smoking rate, compared to the standard run-in group, interaction p = .03. Cigarette craving and salivary cotinine followed a similar pattern, though the latter was evident only among women. Biochemically verified 4-week continuous abstinence rates were higher in the extended run-in group (53%) than the standard run-in group (31%), p = .033.
Conclusions: The extended use of bupropion prior to a quit attempt reduces smoking behavior during the pre quit period and improved short-term abstinence rates. The data are consistent with an extinction-of-reinforcement model and support further investigation of extended run-in bupropion therapy for smoking cessation.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Hurt RD, Sachs DP, Glover ED, et al. A comparison of sustained-release bupropion and placebo for smoking cessation. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:1195–1202. - PubMed
-
- Jorenby DE, Leischow SJ, Nides MA, et al. A controlled trial of sustained-release bupropion, a nicotine patch, or both for smoking cessation. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:685–691. - PubMed
-
- Fiore MC, Jaen CR, Baker TB, et al. Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: 2008 Update. Clinical Practice Guideline. Rockville, MD: U.S. Department of Health and Human Service. Public Health Service; 2008.
-
- Hughes JR, Stead LF, Lancaster T. Antidepressants for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007;1:CD000031. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

