Potential role of (18)F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging in patients presenting with generalized lymphadenopathy
- PMID: 25589803
- PMCID: PMC4290063
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-3919.147532
Potential role of (18)F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging in patients presenting with generalized lymphadenopathy
Abstract
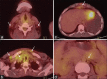
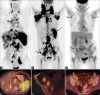
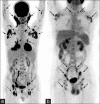
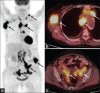
Generalized lymphadenopathy is a common and often vexing clinical problem caused by various inflammatory, infective and malignant diseases. We aimed to review briefly and highlight the potential role of (18)F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose ((18)F-FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in such patients. (18)F-FDG PET/CT can play an important role in the management of generalized lymphadenopathy. It can help in making an etiological diagnosis; can detect extranodal sites of involvement and employed for monitoring response to therapy.
Keywords: 18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography; generalized lymphadenopathy; lymphoma; sarcoidosis; tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
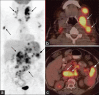
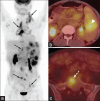
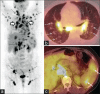
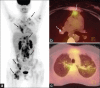
References
-
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): Review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7:19–73. - PubMed
-
- Karunanithi S, Singh H, Sharma P, Naswa N, Kumar R. 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging features of Rosai Dorfman disease: A rare cause of massive generalized lymphadenopathy. Clin Nucl Med. 2014;39:268–9. - PubMed
-
- Raveenthiran V, Dhanalakshmi M, Hayavadana Rao PV, Viswanathan P. Rosai-Dorfman disease: Report of a 3-year-old girl with critical review of treatment options. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2003;13:350–4. - PubMed
-
- Deshayes E, Le Berre JP, Jouanneau E, Vasiljevic A, Raverot G, Seve P. 18F-FDG PET/CT findings in a patient with isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease. Clin Nucl Med. 2013;38:50–2. - PubMed
-
- Huang JY, Lu CC, Hsiao CH, Tzen KY. FDG PET/CT findings in purely cutaneous Rosai-Dorfman disease. Clin Nucl Med. 2011;36:13–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

