Major changes and improvements of dialysis therapy in Korea: review of end-stage renal disease registry
- PMID: 25589829
- PMCID: PMC4293557
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2015.30.1.17
Major changes and improvements of dialysis therapy in Korea: review of end-stage renal disease registry
Abstract
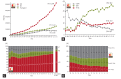
The Korean Society of Nephrology (KSN) launched a nationwide end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patient registry in 1985 called the Insan Prof. Byung-Suk Min Memorial ESRD Patient Registry. KSN members voluntarily participate in this registry, which has been collecting data through the Internet since 2000. The KSN ESRD patient registry data were reviewed to elucidate the major changes and improvements in dialysis therapy in Korea. The data review revealed: a rapid increase in the number of patients with ESRD; an increase in the number of patients with diabetic nephropathy; a decrease in the proportion of patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis; an increase in the role of private dialysis clinics; an increase in the number of elderly patients undergoing dialysis and the number of patients undergoing long-term dialysis; a decrease in mean blood pressure and an increase in pulse pressure; improvement in anemia treatment; improvement in dialysis adequacy; and improvement in the survival of patients undergoing dialysis. In conclusion, improvements have been made in blood pressure control, anemia treatment, and dialysis adequacy despite increases in the number of elderly patients, diabetic patients, and patients on long-term dialysis during the last two decades in Korea.
Keywords: Dialysis registry; Kidney failure, chronic; Peritoneal dialysis; Renal dialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- ESRD Registry Committee, Korean Society of Nephrology. Current renal replacement therapy in Korea 2013 [Internet] Seoul (KR): Korean Society of Nephrology; c2006. [cited 2014 Sep 1]. Available from: http://www.ksn.or.kr.
-
- Untied States renal data system (USRDS) 2013 USRDS annual data report [Internet] Ann Arbor (MI): USRDS; 2013. [cited 2014 Sep 1]. Available from: http://www.usrds.org/adr.htm.
-
- Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy. An overview of regular dialysis treatment in Japan [Internet] Tokyo (JP): Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy; c2007. [cited 2014 Sep 1]. Available from: http://www.jsdt.or.jp.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
