RNA-guided isomerization of uridine to pseudouridine--pseudouridylation
- PMID: 25590339
- PMCID: PMC4615163
- DOI: 10.4161/15476286.2014.972855
RNA-guided isomerization of uridine to pseudouridine--pseudouridylation
Abstract
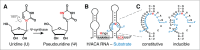
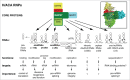
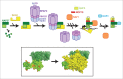
Box H/ACA ribonucleoproteins (RNPs), each consisting of one unique guide RNA and 4 common core proteins, constitute a family of complex enzymes that catalyze, in an RNA-guided manner, the isomerization of uridines to pseudouridines (Ψs) in RNAs, a reaction known as pseudouridylation. Over the years, box H/ACA RNPs have been extensively studied revealing many important aspects of these RNA modifying machines. In this review, we focus on the composition, structure, and biogenesis of H/ACA RNPs. We explain the mechanism of how this enzyme family recognizes and specifies its target uridine in a substrate RNA. We discuss the substrates of box H/ACA RNPs, focusing on rRNA (rRNA) and spliceosomal small nuclear RNA (snRNA). We describe the modification product Ψ and its contribution to RNA function. Finally, we consider possible mechanisms of the bone marrow failure syndrome dyskeratosis congenita and of prostate and other cancers linked to mutations in H/ACA RNPs.
Keywords: DC, dyskeratosis congenita; H/ACA; HH, hoyeraal-hreidarsson syndrome; PIKK, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase; PUA, pseudouridylase and archaeosine transglycosylase; RNA modification; RNA-guided; RNP, ribonucleoprotein; SMN, survival of motor neuron protein; SSD, SHQ1 specific domain; U, uridine; X-DC, X-linked dyskeratosis congenita; dyskeratosis congenita; prostate cancer; pseudouridine; rRNA; rRNA, ribosomal RNA; ribonucleoproteins; sca, small Cajal body; snRNA, small nuclear RNA; sno, small nucleolar; snoRNA; snoRNA, small nucleolar RNA; spliceosomal small nuclear RNA; tRNA, transfer RNA; ψ, pseudouridine, 5-ribosyluracil.
Figures
References
-
- Machnicka MA, Milanowska K, Osman Oglou O, Purta E, Kurkowska M, Olchowik A, Januszewski W, Kalinowski S, Dunin-Horkawicz S, Rother KM, et al. . MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways–2013 update. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41:D262-7; PMID:23118484; http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1007 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davis FF, Allen FW. Ribonucleic acids from yeast which contain a fifth nucleotide. J Biol Chem 1957; 227:907-15; PMID:13463012 - PubMed
-
- Ferre d'Amare A. RNA-modifying enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2003; 13:49-55; PMID:12581659; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0959-440X(02)00002-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Charette M, Gray MW. Pseudouridine in RNA: what, where, how, and why. IUBMB Life 2000; 49:341-51; PMID:10902565; http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/152165400410182 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boschi-Muller S, Motorin Y. Chemistry enters nucleic acids biology: enzymatic mechanisms of RNA modification. Biochem Moscow 2014; 78:1392-404; http://dx.doi.org/10.1134/S0006297913130026 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
