PPM1D regulates p21 expression via dephoshporylation at serine 123
- PMID: 25590690
- PMCID: PMC4612391
- DOI: 10.4161/15384101.2014.994922
PPM1D regulates p21 expression via dephoshporylation at serine 123
Abstract
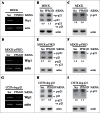
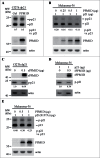
The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 plays a critical role in regulating cell cycle and cell proliferation. We previously cloned the dog p21 gene and found that unlike human p21, dog p21 is expressed as 2 isoforms due to the proline-directed phosphorylation at serine 123 (S123). Here, we identified that PPM1D, also called Wip1 and a Mg(2+)-dependent phosphatase, dephosphorylates dog p21 protein at serine 123. Specifically, we showed that the level of S123-phosphorylated dog p21 is increased by a PPM1D inhibitor in a dose-dependent manner. We also showed that over-expression of PPM1D decreases, whereas knockdown of PPM1D increases, the level of S123-phosphorylated dog p21 regardless of p53. Additionally, in vitro phosphatase assay was performed and showed that phosphorylated S123 in dog p21 is dephosphorylated by recombinant rPPM1D, which contains the catalytic domain of human PPM1D (residue 1-420), but not by the phosphatase dead rPPM1D (D314A). Furthermore, dephosphorylation of S123 by rPPM1D can be abrogated by PPM1D inhibitor or by withdrawal of Mg(2+). Finally, we showed that upon PPM1D inhibition, the level of S123-phosphorylated dog p21 was increased, concomitantly with decreased expression of cyclin A, cyclin B, Rb, and PCNA. Together, our results indicate that PPM1D functions as a phosphatase of dog p21 at serine 123 and plays a role in cell cycle control via p21.
Keywords: ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutated; CDKs, cyclin-dependent kinases; Cip1, Cdk interacting protein 1; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PP2C, type 2C protein phosphatases; PPM1D; PPM1D, Protein phosphatase Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent 1D; WAF1, wild-type p53 activated factor 1; Wip1; Wip1, wild-type p53 induced phosphatase 1; p21; p53; phosphatase.
Figures


References
-
- el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993; 75:817-825; PMID:8242752; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-P - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang J, Cho SJ, Shu L, Yan W, Guerrero T, Kent M, Skorupski K, Chen H, Chen X. Translational repression of p53 by RNPC1, a p53 target overexpressed in lymphomas. Genes & Development 2011; 25:1528-1543; PMID:21764855; http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.2069311 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 1993; 75:805-816; PMID:8242751; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-G - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jung YS, Qian Y, Chen X. Examination of the expanding pathways for the regulation of p21 expression and activity. Cell Signal 2010; 22:1003-1012; PMID:20100570; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.01.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gu Y, Turck CW, Morgan DO. Inhibition of CDK2 activity in vivo by an associated 20K regulatory subunit. Nature 1993; 366:707-710; PMID:8259216; http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/366707a0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
