Elevation of serum immunoglobulin free light chains during the preclinical period of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 25593227
- PMCID: PMC4371213
- DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.140543
Elevation of serum immunoglobulin free light chains during the preclinical period of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Immunoglobulin free light chains (FLC) represent biomarkers of B cell activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and are associated with all-cause mortality in the general population. Our objective was to evaluate the relationships of serum FLC to preclinical disease, RA characteristics, and mortality in RA compared to non-RA subjects.
Methods: A population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota, USA, was performed by crosslinking a large cohort in the general population having available serum FLC measurements with established RA incidence and prevalence cohorts. Serum κ, λ, and total FLC and their trends relative to RA incidence were compared between RA and non-RA subjects. Regression models were used to determine the associations between FLC, disease characteristics, and mortality, testing for differential effects of FLC on mortality in RA.
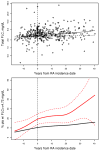
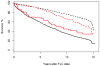
Results: Among 16,609 subjects, 270 fulfilled the criteria for RA at the time of FLC measurement. Mean total FLC were significantly higher in RA compared to non-RA subjects (4.2 vs 3.3 mg/dl, p < 0.001). FLC became elevated 3-5 years before the clinical onset of RA and remained elevated during followup. Polyclonal FLC were found to predict higher mortality in persons with RA, though elevation to the highest decile had a relatively lower effect on mortality in RA compared to non-RA subjects.
Conclusion: Elevation of serum FLC precedes the development of RA and may be useful in monitoring B cell activity and disease progression. FLC are associated with mortality among patients with RA as well as the general population.
Keywords: AUTOIMMUNITY; B CELL; BIOMARKERS; MORTALITY.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum free light chains as biomarkers for systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011 Jun;63(6):891-8. doi: 10.1002/acr.20446. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011. PMID: 21312346
-
Serum immunoglobulin free light chain assessment in rheumatoid arthritis and primary Sjogren's syndrome.Ann Rheum Dis. 2007 Jan;66(1):23-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2006.052159. Epub 2006 Mar 28. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007. PMID: 16569685 Free PMC article.
-
Use of nonclonal serum immunoglobulin free light chains to predict overall survival in the general population.Mayo Clin Proc. 2012 Jun;87(6):517-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.03.009. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012. PMID: 22677072 Free PMC article.
-
[Usefulness of a free light chain immunoassay in serum for the diagnosis and the follow-up of monoclonal gammopathy].Rev Med Interne. 2007 Oct;28(10):689-97. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2007.04.010. Epub 2007 May 25. Rev Med Interne. 2007. PMID: 17566612 Review. French.
-
Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains in the Pathogenesis of Lung Disorders.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017 Aug;16(4):282-288. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28865407 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression and diagnostic value of serum free light chain in lung cancer.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jun 28;49(6):914-920. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.230576. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39311787 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Serum levels of free light chains and syndecan-1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025 May 1;64(5):2422-2431. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae623. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2025. PMID: 39509329 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of serum free light chains as a marker of systemic lupus flare.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Feb;39(2):449-454. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04827-4. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31773496
-
Reduced serum immunoglobulin G concentrations in multiple sclerosis: prevalence and association with disease-modifying therapy and disease course.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2019 Sep 27;12:1756286419878340. doi: 10.1177/1756286419878340. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2019. PMID: 31632461 Free PMC article.
-
Different roles of urinary light chains and serum light chains as potential biomarkers for monitoring disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus.PeerJ. 2022 May 17;10:e13385. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13385. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35602892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC, et al. The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:155–63. - PubMed
-
- Kroot EJ, de Jong BA, van Leeuwen MA, Swinkels H, van den Hoogen FH, van't Hof M, et al. The prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1831–5. - PubMed
-
- Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, de Jong BA, Berglin E, Hallmans G, Wadell G, Stenlund H, et al. Antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptide and IgA rheumatoid factor predict the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2741–9. - PubMed
-
- van der Woude D, Rantapaa-Dahlqvist S, Ioan-Facsinay A, Onnekink C, Schwarte CM, Verpoort KN, et al. Epitope spreading of the anti-citrullinated protein antibody response occurs before disease onset and is associated with the disease course of early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1554–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
