Macrophage sortilin promotes LDL uptake, foam cell formation, and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 25593281
- PMCID: PMC4602371
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.305811
Macrophage sortilin promotes LDL uptake, foam cell formation, and atherosclerosis
Abstract
Rationale: Noncoding gene variants at the SORT1 locus are strongly associated with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, as well as with coronary artery disease. SORT1 encodes a protein called sortilin, and hepatic sortilin modulates LDL metabolism by targeting apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins to the lysosome. Sortilin is also expressed in macrophages, but its role in macrophage uptake of LDL and in atherosclerosis independent of plasma LDL-C levels is unknown.
Objective: To determine the effect of macrophage sortilin expression on LDL uptake, foam cell formation, and atherosclerosis.
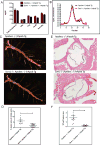
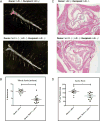
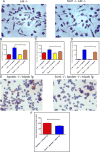
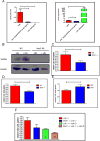
Methods and results: We crossed Sort1(-/-) mice onto a humanized Apobec1(-/-); hAPOB transgenic background and determined that Sort1 deficiency on this background had no effect on plasma LDL-C levels but dramatically reduced atherosclerosis in the aorta and aortic root. To test whether this effect was a result of macrophage sortilin deficiency, we transplanted Sort1(-/-);LDLR(-/-) or Sort1(+/+);LDLR(-/-) bone marrow into Ldlr(-/-) mice and observed a similar reduction in atherosclerosis in mice lacking hematopoetic sortilin without an effect on plasma LDL-C levels. In an effort to determine the mechanism by which hematopoetic sortilin deficiency reduced atherosclerosis, we found no effect of sortilin deficiency on macrophage recruitment or lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine release in vivo. In contrast, sortilin-deficient macrophages had significantly reduced uptake of native LDL ex vivo and reduced foam cell formation in vivo, whereas sortilin overexpression in macrophages resulted in increased LDL uptake and foam cell formation.
Conclusions: Macrophage sortilin deficiency protects against atherosclerosis by reducing macrophage uptake of LDL. Sortilin-mediated uptake of native LDL into macrophages may be an important mechanism of foam cell formation and contributor to atherosclerosis development.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; foam cell; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; macrophage; receptor-mediated endocytosis.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
SORTILIN: many headed hydra.Circ Res. 2015 Feb 27;116(5):764-6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306036. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 25722435 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

