The transcription factor Nerfin-1 prevents reversion of neurons into neural stem cells
- PMID: 25593306
- PMCID: PMC4298133
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.250282.114
The transcription factor Nerfin-1 prevents reversion of neurons into neural stem cells
Abstract
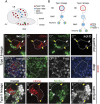
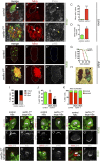
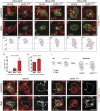
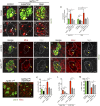
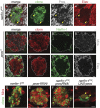
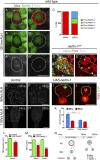
Cellular dedifferentiation is the regression of a cell from a specialized state to a more multipotent state and is implicated in cancer. However, the transcriptional network that prevents differentiated cells from reacquiring stem cell fate is so far unclear. Neuroblasts (NBs), the Drosophila neural stem cells, are a model for the regulation of stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Here we show that the Drosophila zinc finger transcription factor Nervous fingers 1 (Nerfin-1) locks neurons into differentiation, preventing their reversion into NBs. Following Prospero-dependent neuronal specification in the ganglion mother cell (GMC), a Nerfin-1-specific transcriptional program maintains differentiation in the post-mitotic neurons. The loss of Nerfin-1 causes reversion to multipotency and results in tumors in several neural lineages. Both the onset and rate of neuronal dedifferentiation in nerfin-1 mutant lineages are dependent on Myc- and target of rapamycin (Tor)-mediated cellular growth. In addition, Nerfin-1 is required for NB differentiation at the end of neurogenesis. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis show that Nerfin-1 administers its function by repression of self-renewing-specific and activation of differentiation-specific genes. Our findings support the model of bidirectional interconvertibility between neural stem cells and their post-mitotic progeny and highlight the importance of the Nerfin-1-regulated transcriptional program in neuronal maintenance.
Keywords: Drosophila; cancer; central nervous system; dedifferentiation; neuroblasts; stem cells.
© 2015 Froldi et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prevention of medulla neuron dedifferentiation by Nerfin-1 requires inhibition of Notch activity.Development. 2017 Apr 15;144(8):1510-1517. doi: 10.1242/dev.141341. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Development. 2017. PMID: 28242614
-
bHLH-O proteins balance the self-renewal and differentiation of Drosophila neural stem cells by regulating Earmuff expression.Dev Biol. 2017 Nov 15;431(2):239-251. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.09.011. Epub 2017 Sep 9. Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 28899667 Free PMC article.
-
The Scalloped and Nerfin-1 Transcription Factors Cooperate to Maintain Neuronal Cell Fate.Cell Rep. 2018 Nov 6;25(6):1561-1576.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.038. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30404010
-
Drosophila neural stem cells: cell cycle control of self-renewal, differentiation, and termination in brain development.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2011;53:529-46. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-19065-0_21. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2011. PMID: 21630158 Review.
-
Control of neural stem cell self-renewal and differentiation in Drosophila.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jan;359(1):33-45. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1914-9. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 24902665 Review.
Cited by
-
The retromer complex safeguards against neural progenitor-derived tumorigenesis by regulating Notch receptor trafficking.Elife. 2018 Sep 4;7:e38181. doi: 10.7554/eLife.38181. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30176986 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive temporal patterning gene network in Drosophila medulla neuroblasts revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing.Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 10;13(1):1247. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28915-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35273186 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genomic enhancers through spatial integration of single-cell transcriptomics and epigenomics.Mol Syst Biol. 2020 May;16(5):e9438. doi: 10.15252/msb.20209438. Mol Syst Biol. 2020. PMID: 32431014 Free PMC article.
-
Histidine is selectively required for the growth of Myc-dependent dedifferentiation tumours in the Drosophila CNS.EMBO J. 2019 Apr 1;38(7):e99895. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899895. Epub 2019 Feb 25. EMBO J. 2019. PMID: 30804004 Free PMC article.
-
Her6 and Prox1a are novel regulators of photoreceptor regeneration in the zebrafish retina.PLoS Genet. 2023 Nov 6;19(11):e1011010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011010. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37930995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bello BC, Hirth F, Gould AP. 2003. A pulse of the Drosophila Hox protein Abdominal-A schedules the end of neural proliferation via neuroblast apoptosis. Neuron 37: 209–219. - PubMed
-
- Bello B, Reichert H, Hirth F. 2006. The brain tumor gene negatively regulates neural progenitor cell proliferation in the larval central brain of Drosophila. Development 133: 2639–2648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
