Defective PDI release from platelets and endothelial cells impairs thrombus formation in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
- PMID: 25593336
- PMCID: PMC4351508
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-08-597419
Defective PDI release from platelets and endothelial cells impairs thrombus formation in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
Abstract
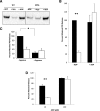
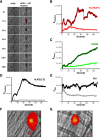
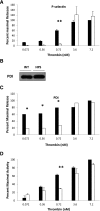
Protein disulfide isomerase (PDI), secreted from platelets and endothelial cells after injury, is required for thrombus formation. The effect of platelet and endothelial cell granule contents on PDI-mediated thrombus formation was studied by intravital microscopy using a mouse model of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome in which platelet dense granules are absent. Platelet deposition and fibrin generation were nearly absent, and extracellular PDI was significantly reduced in HPS6(-/-) mice after vascular injury. HPS6(-/-) platelets displayed impaired PDI secretion and impaired exocytosis of α granules, lysosomes, and T granules due to decreased sensitivity to thrombin, but these defects could be corrected by addition of subthreshold amounts of adenosine 5'-diphosphate (ADP). Human Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome platelets demonstrated similar characteristics. Infusion of wild-type platelets rescued thrombus formation in HPS6(-/-) mice. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells in which the HPS6 gene was silenced displayed impaired PDI secretion and exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies. Defective thrombus formation in Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, associated with impaired exocytosis of residual granules in endothelial cells and platelets, the latter due to deficiency of ADP, is characterized by a defect in T granule secretion, a deficiency in extracellular PDI secretion, and impaired fibrin generation and platelet aggregation. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome is an example of a hereditary disease whereby impaired PDI secretion contributes to a bleeding phenotype.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures




Comment in
-
Defective platelet autocrine signaling in HPS.Blood. 2015 Mar 5;125(10):1515-6. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-01-616284. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25745182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Logan LJ, Rapaport SI, Maher I. Albinism and abnormal platelet function. N Engl J Med. 1971;284(24):1340–1345. - PubMed
-
- Hardisty RM, Mills DC, Ketsa-Ard K. The platelet defect associated with albumism. Br J Haematol. 1972;23(6):679–692. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Q, Zhao B, Li W, et al. Ru2 and Ru encode mouse orthologs of the genes mutated in human Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome types 5 and 6. Nat Genet. 2003;33(2):145–153. - PubMed
-
- Gautam R, Chintala S, Li W, et al. The Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome 3 (cocoa) protein is a component of the biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-2 (BLOC-2). J Biol Chem. 2004;279(13):12935–12942. - PubMed
-
- Di Pietro SM, Falcón-Pérez JM, Dell’Angelica EC. Characterization of BLOC-2, a complex containing the Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome proteins HPS3, HPS5 and HPS6. Traffic. 2004;5(4):276–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

