Clinical detection and characterization of bacterial pathogens in the genomics era
- PMID: 25593594
- PMCID: PMC4295418
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-014-0114-2
Clinical detection and characterization of bacterial pathogens in the genomics era
Abstract
The availability of genome sequences obtained using next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized the field of infectious diseases. Indeed, more than 38,000 bacterial and 5,000 viral genomes have been sequenced to date, including representatives of all significant human pathogens. These tremendous amounts of data have not only enabled advances in fundamental biology, helping to understand the pathogenesis of microorganisms and their genomic evolution, but have also had implications for clinical microbiology. Here, we first review the current achievements of genomics in the development of improved diagnostic tools, including those that are now available in the clinic, such as the design of PCR assays for the detection of microbial pathogens, virulence factors or antibiotic-resistance determinants, or the design of optimized culture media for 'unculturable' pathogens. We then review the applications of genomics to the investigation of outbreaks, either through the design of genotyping assays or the direct sequencing of the causative strains. Finally, we discuss how genomics might change clinical microbiology in the future.
Figures

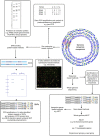
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, Alvarado M, Anderson HR, Anderson LM, Andrews KG, Atkinson C, Baddour LM, Barker-Collo S, Bartels DH, Bell ML, Benjamin EJ, Bennett D, Bhalla K, Bikbov B, Bin Abdulhak A, Birbeck G, Blyth F, Bolliger I, Boufous S, Bucello C, Burch M, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095–2128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Relman DA, Falkow S. Identification of uncultured microorganisms: expanding the spectrum of characterized microbial pathogens. Infect Agents Dis. 1992;1:245–253. - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann RD, Adams MD, White O, Clayton RA, Kirkness EF, Kerlavage AR, Bult CJ, Tomb JF, Dougherty BA, Merrick JM, McKenney K, Sutton G, FitzHugh W, Fields C, Gocyne JD, Scott J, Shirley R, Liu L-I, Glodek A, Kelley JM, Weidman JF, Phillips CA, Spriggs T, Hedblom E, Cotton MD, Utterback TR, Hanna MC, Nguyen DT, Saudek DM, Brandon RC, et al. Whole-genome random sequençing and assembly of Hamophilus influenzaeRd. Science. 1995;269:496–512. doi: 10.1126/science.7542800. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Logares R, Haverkamp TH, Kumar S, Lanzen A, Nederbragt AJ, Quince C, Kauserud H. Environmental microbiology through the lens of high-throughput DNA sequencing: synopsis of current platforms and bioinformatics approaches. J Microbiol Methods. 2012;91:106–113. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.07.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

