The contrasting phylodynamics of human influenza B viruses
- PMID: 25594904
- PMCID: PMC4383373
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.05055
The contrasting phylodynamics of human influenza B viruses
Abstract
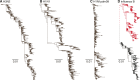
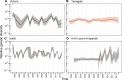
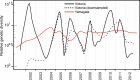
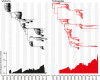
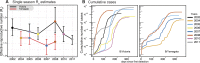
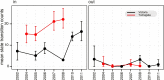
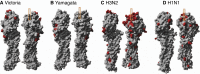
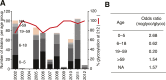
A complex interplay of viral, host, and ecological factors shapes the spatio-temporal incidence and evolution of human influenza viruses. Although considerable attention has been paid to influenza A viruses, a lack of equivalent data means that an integrated evolutionary and epidemiological framework has until now not been available for influenza B viruses, despite their significant disease burden. Through the analysis of over 900 full genomes from an epidemiological collection of more than 26,000 strains from Australia and New Zealand, we reveal fundamental differences in the phylodynamics of the two co-circulating lineages of influenza B virus (Victoria and Yamagata), showing that their individual dynamics are determined by a complex relationship between virus transmission, age of infection, and receptor binding preference. In sum, this work identifies new factors that are important determinants of influenza B evolution and epidemiology.
Keywords: antigenic drift; epidemiology; evolution; evolutionary biology; genomics; human; infectious disease; influenza virus; microbiology; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures








References
-
- Anderson R, May R. Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control. Oxford: Oxford science publications (OUP); 1992.
-
- Bahl J, Krauss S, Kühnert D, Fourment M, Raven G, Pryor SP, Niles LJ, Danner A, Walker D, Mendenhall IH, Su YC, Dugan VG, Halpin RA, Stockwell TB, Webby RJ, Wentworth DE, Drummond AJ, Smith GJ, Webster RG. Influenza A virus migration and persistence in North American wild birds. PLOS Pathogens. 2013;9:e1003570. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003570. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bahl J, Nelson MI, Chan KH, Chen R, Vijaykrishna D, Halpin RA, Stockwell TB, Lin X, Wentworth DE, Ghedin E, Guan Y, Peiris JS, Riley S, Rambaut A, Holmes EC, Smith GJ. Temporally structured metapopulation dynamics and persistence of influenza A H3N2 virus in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA. 2011;108:19359–19364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109314108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

