Design and development of a content-based medical image retrieval system for spine vertebrae irregularity
- PMID: 25595511
- PMCID: PMC4349791
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-925X-14-6
Design and development of a content-based medical image retrieval system for spine vertebrae irregularity
Abstract
Background: Content-based medical image retrieval (CBMIR) system enables medical practitioners to perform fast diagnosis through quantitative assessment of the visual information of various modalities.
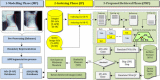
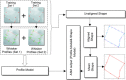
Methods: In this paper, a more robust CBMIR system that deals with both cervical and lumbar vertebrae irregularity is afforded. It comprises three main phases, namely modelling, indexing and retrieval of the vertebrae image. The main tasks in the modelling phase are to improve and enhance the visibility of the x-ray image for better segmentation results using active shape model (ASM). The segmented vertebral fractures are then characterized in the indexing phase using region-based fracture characterization (RB-FC) and contour-based fracture characterization (CB-FC). Upon a query, the characterized features are compared to the query image. Effectiveness of the retrieval phase is determined by its retrieval, thus, we propose an integration of the predictor model based cross validation neural network (PMCVNN) and similarity matching (SM) in this stage. The PMCVNN task is to identify the correct vertebral irregularity class through classification allowing the SM process to be more efficient. Retrieval performance between the proposed and the standard retrieval architectures are then compared using retrieval precision (Pr@M) and average group score (AGS) measures.
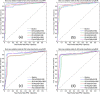
Results: Experimental results show that the new integrated retrieval architecture performs better than those of the standard CBMIR architecture with retrieval results of cervical (AGS > 87%) and lumbar (AGS > 82%) datasets.
Conclusions: The proposed CBMIR architecture shows encouraging results with high Pr@M accuracy. As a result, images from the same visualization class are returned for further used by the medical personnel.
Figures









Similar articles
-
On the creation of a segmentation library for digitized cervical and lumbar spine radiographs.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2011 Jun;35(4):251-65. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2010.11.006. Epub 2011 Mar 5. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2011. PMID: 21377835
-
Interactive radiographic image retrieval system.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017 Feb;139:209-220. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.10.023. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28187892
-
A novel biomedical image indexing and retrieval system via deep preference learning.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 May;158:53-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Feb 6. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 29544790
-
Optimal query-based relevance feedback in medical image retrieval using score fusion-based classification.J Digit Imaging. 2015 Apr;28(2):160-78. doi: 10.1007/s10278-014-9730-z. J Digit Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25246167 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Review: Segmentation and classification methods of 3D medical images].Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2002 Mar;26(3):197-206. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 16104307 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Statistical Shape and Appearance Models: Development Towards Improved Osteoporosis Care.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021 Dec;19(6):676-687. doi: 10.1007/s11914-021-00711-w. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021. PMID: 34773211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Analysis on Down-Regulated Images of Macrophage Scavenger Receptor.Pharm Res. 2017 Oct;34(10):2066-2074. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2211-6. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28653157 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Classification Results Accuracy for CT Soft Tissue and Bone Reconstructions in Detecting the Porosity of a Spongy Tissue.J Clin Med. 2022 Aug 3;11(15):4526. doi: 10.3390/jcm11154526. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35956142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aouache M, Hussain A, Samad SA. A new approach for noise reduction in spine radiograph images using a non-linear contrast adjustment scheme based adaptive factor. Sci Res Essays. 2011;6(20):4246–58.
-
- Chi-Ren S, Carla EB, Avinash CK, Akio K, Alex MA, Lynn AB. ASSERT: a physician-in-the-loop content-based retrieval system for HRCT image databases. Comput Vis Image Underst. 1999;75:111–32. doi: 10.1006/cviu.1999.0768. - DOI
-
- Tang LHY, Hanka R, Horace HS. A review of intelligent content-based indexing and browsing of medical images. Health Informatics J. 1999;5:40–9. doi: 10.1177/146045829900500107. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

