Listeria phage and phage tail induction triggered by components of bacterial growth media (phosphate, LiCl, nalidixic acid, and acriflavine)
- PMID: 25595760
- PMCID: PMC4345357
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.03235-14
Listeria phage and phage tail induction triggered by components of bacterial growth media (phosphate, LiCl, nalidixic acid, and acriflavine)
Abstract
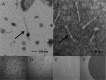
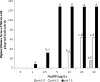
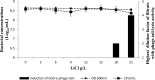
The detection of Listeria monocytogenes from food is currently carried out using a double enrichment. For the ISO methodology, this double enrichment is performed using half-Fraser and Fraser broths, in which the overgrowth of L. innocua can occur in samples where both species are present. In this study, we analyzed the induction of phages and phage tails of Listeria spp. in these media and in two brain heart infusion (BHI) broths (BHIM [bioMérieux] and BHIK [Biokar]) to identify putative effectors. It appears that Na2HPO4 at concentrations ranging from 1 to 40 g/liter with an initial pH of 7.5 can induce phage or phage tail production of Listeria spp., especially with 10 g/liter of Na2HPO4 and a pH of 7.5, conditions present in half-Fraser and Fraser broths. Exposure to LiCl in BHIM (18 to 21 g/liter) can also induce phage and phage tail release, but in half-Fraser and Fraser broths, the concentration of LiCl is much lower (3 g/liter). Low phage titers were induced by acriflavine and/or nalidixic acid. We also show that the production of phages and phage tails can occur in half-Fraser and Fraser broths. This study points out that induction of phages and phage tails could be triggered by compounds present in enrichment media. This could lead to a false-negative result for the detection of L. monocytogenes in food products.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ryser ET, Marth EH. 1999. Listeria, listeriosis and food safety, 2nd ed. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, NY.
-
- . 2004. Microbiology of food and animal feeding stuffs. Horizontal method for detection and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes, part 1: detection method. Amendment 1: modification of the isolation media and the haemolysis test, and inclusion of precision data. EN ISO 11290-1:1996/A1:2004. European Committee for Standardization, Brussels, Belgium.
-
- Walsh D, Duffy G, Sheridan JJ, Blair IS, McDowell DA. 1998. Comparison of selective and non-selective media for the isolation of Listeria species from retail foods. J Food Saf 18:85–89. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4565.1998.tb00205.x. - DOI
-
- Harvey J, Gilmour A. 2001. Characterization of recurrent and sporadic Listeria monocytogenes isolates from raw milk and nondairy foods by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, monocin typing, plasmid profiling, and cadmium and antibiotic resistance determination. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:840–847. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.2.840-847.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

