CD36 is indispensable for thermogenesis under conditions of fasting and cold stress
- PMID: 25596128
- PMCID: PMC4344115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.12.124
CD36 is indispensable for thermogenesis under conditions of fasting and cold stress
Abstract
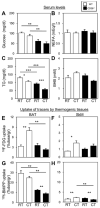
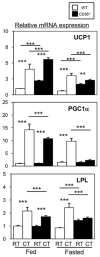
Hypothermia can occur during fasting when thermoregulatory mechanisms, involving fatty acid (FA) utilization, are disturbed. CD36/FA translocase is a membrane protein which facilitates membrane transport of long-chain FA in the FA consuming heart, skeletal muscle (SkM) and adipose tissues. It also accelerates uptake of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein by brown adipose tissue (BAT) in a cold environment. In mice deficient for CD36 (CD36(-/-) mice), FA uptake is markedly reduced with a compensatory increase in glucose uptake in the heart and SkM, resulting in lower levels of blood glucose especially during fasting. However, the role of CD36 in thermogenic activity during fasting remains to be determined. In fasted CD36(-/-) mice, body temperature drastically decreased shortly after cold exposure. The hypothermia was accompanied by a marked reduction in blood glucose and in stores of triacylglycerols in BAT and of glycogen in glycolytic SkM. Biodistribution analysis using the FA analogue (125)I-BMIPP and the glucose analogue (18)F-FDG revealed that uptake of FA and glucose was severely impaired in BAT and glycolytic SkM in cold-exposed CD36(-/-) mice. Further, induction of the genes of thermogenesis in BAT was blunted in fasted CD36(-/-) mice after cold exposure. These findings strongly suggest that CD36(-/-) mice exhibit pronounced hypothermia after fasting due to depletion of energy storage in BAT and glycolytic SkM and to reduced supply of energy substrates to these tissues. Our study underscores the importance of CD36 for nutrient homeostasis to survive potentially life-threatening challenges, such as cold and starvation.
Keywords: Brown adipose tissue; CD36; Fatty acid; Hypothermia; Skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

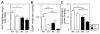
References
-
- Cannon B, Nedergaard J. Brown adipose tissue: function and physiological significance. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:277–359. - PubMed
-
- Klingenspor M. Cold-induced recruitment of brown adipose tissue thermo-genesis. Exp Physiol. 2003;88:141–148. - PubMed
-
- Syamsunarno MR, Iso T, Yamaguchi A, Hanaoka H, Putri M, Obokata M, Sunaga H, Koitabashi N, Matsui H, Maeda K, Endo K, Tsushima Y, Yokoyama T, Kurabayashi M. Fatty acid binding protein 4 and 5 play a crucial role in thermogenesis under the conditions of fasting and cold stress. PLoS One. 2014;9:e90825. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haman F. Shivering in the cold: from mechanisms of fuel selection to survival. J Appl Physiol. 2006;100:1702–1708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

