Stability of P50 auditory sensory gating during sleep from infancy to 4 years of age
- PMID: 25596494
- PMCID: PMC4330098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bandc.2014.12.004
Stability of P50 auditory sensory gating during sleep from infancy to 4 years of age
Abstract
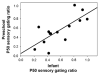
The stability of cerebral inhibition was assessed across early childhood using a paired-click auditory sensory gating paradigm. The P50 ERP was measured during REM (or its infant analogue, active sleep) and NREM sleep in 14 children at approximately 3 months of age and again at approximately 4 years of age. Evoked response amplitudes, latencies, and the S2/S1 ratio of the amplitudes of the evoked responses were compared between the two visits. Significant reliability was found for the S2/S1 ratio (r = .73, p = .003) during REM but not non REM sleep (r = -.05, p = .88). A significant stimulus number by sleep stage interaction (F(1,12) = 17.1, p = .001) demonstrated that the response to the second stimulus decreased during REM but not NREM sleep. These findings suggest that this measure is stable during REM sleep across early childhood, is not affected by age, and is sleep-state dependent. P50 sensory gating is a biomarker which, if used properly, may provide a mechanism to further explore changes in the developing brain or may help with early screening for psychiatric illness vulnerability.
Keywords: Auditory sensory gating; Infant; P50; Sleep.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adler LE, Gerhardt GA, Franks R, Baker N, Nagamoto H, Drebing C, et al. Sensory physiology and catecholamines in schizophrenia and mania. Psychiatry Research. 1990;31(3):297–309. - PubMed
-
- Adler LE, Hoffer L, Nagamot HT, Waldo MC, Kisley MA, Griffith JM. Yohimbine impairs P50 auditory sensory gating in normal subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1994;10(4):249–257. - PubMed
-
- Adler LE, Pachtman E, Franks RD, Pecevich M, Waldo MC, Freedman R. Neurophysiological evidence for a defect in neuronal mechanisms involved in sensory gating in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry. 1982;6 < www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7104417>. - PubMed
-
- Brinkman MJR, Stauder JEA. Development and gender in the P50 paradigm. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2007;118(7):1517–1524. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2007.04.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ceponiene R, Kushnerenko E, Fellman V, Renlund M, Suominen K, Naatanen R. Event-related potential features indexing central auditory discrimination by newborns. Brain Research Cognitive Brain Research. 2012;13:101–103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HD058033/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 MH080859/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH086383/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH080859/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- TR000154/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 HD058033/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- MH086383/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- MH101295/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH056539/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH056539/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

