Resistance strength training exercise in children with spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 25597614
- PMCID: PMC4506899
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.24568
Resistance strength training exercise in children with spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
Introduction: Preliminary evidence in adults with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) and in SMA animal models suggests exercise has potential benefits in improving or stabilizing muscle strength and motor function.
Methods: We evaluated feasibility, safety, and effects on strength and motor function of a home-based, supervised progressive resistance strength training exercise program in children with SMA types II and III. Up to 14 bilateral proximal muscles were exercised 3 times weekly for 12 weeks.
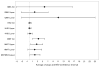
Results: Nine children with SMA, aged 10.4 ± 3.8 years, completed the resistance training exercise program. Ninety percent of visits occurred per protocol. Training sessions were pain-free (99.8%), and no study-related adverse events occurred. Trends in improved strength and motor function were observed.
Conclusions: A 12-week supervised, home-based, 3-day/week progressive resistance training exercise program is feasible, safe, and well tolerated in children with SMA. These findings can inform future studies of exercise in SMA.
Keywords: home-based exercise program; neuromuscular disorder; progressive resistance training exercise; spinal muscular atrophy; strength training exercise.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Zerres K, Rudnik-Schoneborn S. Natural history in proximal spinal muscular atrophy. Clinical analysis of 445 patients and suggestions for a modification of existing classifications. Arch Neurol. 1995;52(5):518–23. - PubMed
-
- Russman BS, Buncher CR, White M, Samaha FJ, Iannaccone ST. Function changes in spinal muscular atrophy II and III. The DCN/SMA Group. Neurology. 1996;47(4):973–6. - PubMed
-
- Zerres K, Rudnik-Schoneborn S, Forrest E, Lusakowska A, Borkowska J, Hausmanowa-Petrusewicz I. A collaborative study on the natural history of childhood and juvenile onset proximal spinal muscular atrophy (type II and III SMA): 569 patients. J Neurol Sci. 1997;146(1):67–72. - PubMed
-
- Wang HY, Yang YH, Jong YJ. Evaluation of muscle strength in patients with spinal muscular atrophy. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2002;18(5):241–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 8KL2TR000104/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025763/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD054599/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 RR025763/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000105/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- KL2RR025763/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 8UL1TR000105/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HD054599/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD069045/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001067/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

