Evolutionary history and global spread of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing lineage
- PMID: 25599400
- PMCID: PMC11044984
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3195
Evolutionary history and global spread of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis Beijing lineage
Abstract
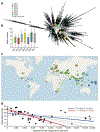
Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains of the Beijing lineage are globally distributed and are associated with the massive spread of multidrug-resistant (MDR) tuberculosis in Eurasia. Here we reconstructed the biogeographical structure and evolutionary history of this lineage by genetic analysis of 4,987 isolates from 99 countries and whole-genome sequencing of 110 representative isolates. We show that this lineage initially originated in the Far East, from where it radiated worldwide in several waves. We detected successive increases in population size for this pathogen over the last 200 years, practically coinciding with the Industrial Revolution, the First World War and HIV epidemics. Two MDR clones of this lineage started to spread throughout central Asia and Russia concomitantly with the collapse of the public health system in the former Soviet Union. Mutations identified in genes putatively under positive selection and associated with virulence might have favored the expansion of the most successful branches of the lineage.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
P. Supply is a consultant for Genoscreen. C.A.-B. and C.W. were or are employees of the same company. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
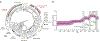

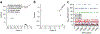
References
-
- Global Tuberculosis Report. (World Health Organization, Geneva, 2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

