Pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of surface engineered carbon nanotubes
- PMID: 25601411
- PMCID: PMC7108288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drudis.2015.01.006
Pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of surface engineered carbon nanotubes
Abstract
Surface engineered carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are attracting recent attention of scientists owing to their vivid biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. The focus of this review is to highlight the important role of surface engineered CNTs in the highly challenging but rewarding area of nanotechnology. The major strength of this review lies in highlighting the exciting applications of CNTs to boost the research efforts, which unfortunately are otherwise scattered in the literature making the reading non-coherent and non-homogeneous.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

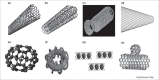
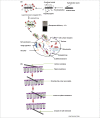

References
-
- Gupta R. Fucosylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes for Kupffer cells targeting for the treatment of cytokine-induced liver damage. Pharm. Res. 2013;31:322–334. - PubMed
-
- Brahmachari S. Biotinylated amphiphile-single walled carbon nanotubes conjugate for target-specific delivery to cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2014;2:1160–1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

