Pharmacotherapy for anxiety and comorbid alcohol use disorders
- PMID: 25601826
- PMCID: PMC8931612
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007505.pub2
Pharmacotherapy for anxiety and comorbid alcohol use disorders
Abstract
Background: Anxiety disorders are a potentially disabling group of disorders that frequently co-occur with alcohol use disorders. Comorbid anxiety and alcohol use disorders are associated with poorer outcomes, and are difficult to treat with standard psychosocial interventions. In addition, improved understanding of the biological basis of the conditions has contributed to a growing interest in the use of medications for the treatment of people with both diagnoses.
Objectives: To assess the effects of pharmacotherapy for treating anxiety in people with comorbid alcohol use disorders, specifically: to provide an estimate of the overall effects of medication in improving treatment response and reducing symptom severity in the treatment of anxiety disorders in people with comorbid alcohol use disorders; to determine whether specific medications are more effective and tolerable than other medications in the treatment of particular anxiety disorders; and to identify which factors (clinical, methodological) predict response to pharmacotherapy for anxiety disorders.
Search methods: Review authors searched the specialized registers of The Cochrane Collaboration Depression, Anxiety and Neurosis Review Group (CCDANCTR, to January 2014) and the Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group (CDAG, to March 2013) for eligible trials. These registers contain reports of relevant randomized controlled trials (RCT) from: the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, all years), MEDLINE (1950 to date), EMBASE (1974 to date) and PsycINFO (1967 to date). Review authors ran complementary searches on EMBASE, PubMed, PsycINFO and the Alcohol and Alcohol Problems Science Database (ETOH) (to August 2013). We located unpublished trials through the National Institutes of Health (NIH) RePORTER service and the World Health Organization (WHO) International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (to August 2013). We screened reference lists of retrieved articles for additional studies.
Selection criteria: All true RCTs of pharmacotherapy for treating anxiety disorders with comorbid alcohol use disorders. Trials assessing drugs administered for the treatment of drinking behaviour, such as naltrexone, disulfiram and acomprosate were not eligible for inclusion in this systematic review.
Data collection and analysis: A systematic review is a standardised evaluation of all research studies that address a particular clinical issue.Two review authors independently assessed RCTs for inclusion in the review, collated trial data and assessed trial quality. We contacted investigators to obtain missing data. We calculated categorical and continuous treatment effect estimates and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) for treatment using a random-effects model with effect-size variability expressed using Chi(2) and I(2) heterogeneity statistics.
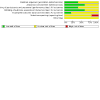
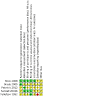
Main results: We included five placebo-controlled pharmacotherapy RCTs (with 290 participants) in the review. Most of the trials provided little information on how randomization was performed or on whether both participants and study personnel were blinded to the intervention. Two of the three trials reporting superiority of medication compared with placebo on anxiety symptom outcomes were industry funded. We regarded one trial as being at high risk of bias due to selective reporting.Study participants had Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) III- and DSM IV-diagnosed alcohol use disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (two studies), social anxiety disorder (SAD; two studies) or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD; one study). Four trials assessed the efficacy of the selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors (SSRIs: sertraline, paroxetine); one RCT investigated the efficacy of buspirone, a 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) partial agonist. Treatment duration lasted between eight and 24 weeks. Overall, 70% of participants included in the review were male.There was very low quality evidence for an effect of paroxetine on global clinical response to treatment, as assessed by the Clinical Global Impressions - Improvement scale (CGI-I). Global clinical response was observed in more than twice as many participants with paroxetine than with placebo (57.7% with paroxetine versus 25.8% with placebo; risk ratio (RR) 2.23, 95% CI 1.13 to 4.41; 2 trials, 57 participants). However, there was substantial uncertainty regarding the size of the effect of paroxetine due to the small number of studies providing data on clinically diverse patient samples. The second primary outcome measure was reduction of anxiety symptom severity. Although study investigators reported that buspirone (one trial) was superior to placebo in reducing the severity of anxiety symptoms over 12 weeks, no evidence of efficacy was observed for paroxetine (mean difference (MD) -14.70, 95% CI -33.00 to 3.60, 2 trials, 44 participants) and sertraline (one trial). Paroxetine appeared to be equally effective in reducing the severity of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms as the tricyclic antidepressant desipramine in one RCT. The maximal reduction in anxiety disorder symptom severity was achieved after six weeks with paroxetine (two RCTs) and 12 weeks with buspirone (one RCT), with maintenance of medication efficacy extending to 16 with paroxetine and 24 weeks with buspirone. There was no evidence of an effect for any of the medications tested on abstinence from alcohol use or depression symptoms. There was very low quality evidence that paroxetine was well tolerated, based on drop-out due to treatment-emergent adverse effects. Nevertheless, levels of treatment discontinuation were high, with 43.1% of the participants in the studies withdrawing from medication treatment. Certain adverse effects, such as sexual problems, were commonly reported after treatment with paroxetine and sertraline.
Authors' conclusions: The evidence-base for the effectiveness of medication in treating anxiety disorders and comorbid alcohol use disorders is currently inconclusive. There was a small amount of evidence for the efficacy of medication, but this was limited and of very low quality. The majority of the data for the efficacy and tolerability of medication were for SSRIs; there were insufficient data to establish differences in treatment efficacy between medication classes or patient subgroups. There was a small amount of very low quality evidence that medication was well tolerated. There was no evidence that alcohol use was responsive to medication.Large, rigorously conducted RCTs would help supplement the small evidence-base for the efficacy and tolerability of pharmacotherapy for anxiety and comorbid alcohol use disorders. Further research on patient subgroups who may benefit from pharmacological treatment, as well as novel pharmacological interventions, is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest for individual review authors:
Jonathan Ipser has no known conflicts of interest.
Don Wilson is employed by the University of Cape Town and the Western Cape Provincial government. As part of his duties, he occasionally conducts clinical trials, some of which are funded by pharmaceutical companies (including GlaxoSmithKline and Organon). He has presented on behalf of Sanofi‐Synthélabo and Eli Lilly in the past. He has previously participated in industry‐sponsored trials in mood disorders. From 2011‐2014, Dr. Wilson received no research grants or consultancy honoraria. Dr. Wilson was involved in a Servier‐sponsored trial of agomelatine for depression, which ended in 2014, for which his department/faculty received reimbursement. He also gave lectures at meetings sponsored by Sanofi‐Synthélabo and Eli Lilly.
Taiwo Akindipe has no known conflicts of interest.
Carli Sager is currently contracted to Parexel International and sub contracted to MSD and Eli Lilly. Carli Sager had no known conflicts of interest while retrieving studies for inclusion in this review.
Dan Stein received research grants or consultancy honoraria (or both) from AMBRF, Biocodex, Cipla, Lundbeck, National Responsible Gambling Foundation, Novartis, Servier and Sun from 2011‐2014.
Figures












Comment in
-
Pharmacotherapy: anxiety and comorbid alcohol use.Nurs Times. 2016 Mar 23-Apr 5;112(12-13):24. Nurs Times. 2016. PMID: 27180463 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Book 2008 {published data only}
-
- Thomas SE, Randall PK, Book SW, Randall CL. A complex relationship between co-occurring social anxiety and alcohol use disorders: what effect does treating social anxiety have on drinking? Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32(1):77-84. - PubMed
Brady 2005 {published data only}
-
- Back SE, Brady KT, Sonne SC, Verduin ML. Symptom improvement in co-occurring PTSD and alcohol dependence. Journal of Nervous and Mental Diseases 2006;194(9):690-6. - PubMed
-
- Brady KT, Sonne S, Anton RF, Randall CL, Back SE, Simpson K. Sertraline in the treatment of co-occurring alcohol dependence and posttraumatic stress disorder. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2005;29(3):395-401. - PubMed
-
- Brady KT, Sonne SC, Killeen T, Simpson K, Randall C, Back SE, et al. Sertraline in comorbid PTSD/alcohol dependence. Proceedings of the 65th Annual Scientific Meeting of the College on Problems of Drug Dependence; 2003 Jun 14-19; Florida 2003.
-
- Labbate LA, Sonne SC, Randal CL, Anton RF, Brady KT. Does comorbid anxiety or depression affect clinical outcomes in patients with post-traumatic stress disorder and alcohol use disorders? Comprehensive Psychiatry 2004;45(4):304-10. - PubMed
-
- Sonne SC, Back SE, Diaz Zuniga C, Randall CL, Brady KT. Gender differences in individuals with comorbid alcohol dependence and post-traumatic stress disorder. American Journal on Addictions 2003;12(5):412-23. - PubMed
Petrakis 2012 {published data only}
-
- Petrakis I, Jane JS, O'Brien E, Keegan K, Ralevski E, Desai N. Effect of depression on outcomes in a clinical trail evaluating antidepressants +/- naltrexone for treatment of alcohol dependence and PTSD. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37:19A.
Randall 2001b {published data only}
-
- Randall CL, Johnson MR, Thevos AK, Sonne SC, Thomas SE, Willard SL, et al. Paroxetine for social anxiety and alcohol use in dual-diagnosed patients. Depression and Anxiety 2001;14(4):255-62. - PubMed
Tollefson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Tollefson GD, Lancaster SP, Montague-Clouse J. The association of buspirone and its metabolite 1-pyrimidinylpiperazine in theremission of comorbid anxiety with depressive features and alcohol dependency. Psychopharmacology Bulletin 1991;27(2):163-70. - PubMed
-
- Tollefson GD, Montague-Clouse J, Lancaster SP. Buspirone in comorbid alcohol dependency and generalized anxiety disorders. Drug Therapeutics 1990;20 Suppl:35-51.
-
- Tollefson GD, Montague-Clouse J, Tollefson SL. Treatment of comorbid generalized anxiety in a recently detoxified alcoholic population with a selective serotonergic drug (buspirone). Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1992;12(1):19-26. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Batki 2011 {published data only}
-
- Batki SL, Lasher BA, Heinz AJ, Herbst E, Metzler T, Prathikanti S, et al. Risk-taking, impulsivity, memory and executive functioning as outcome predictors in a trial of topiramate for alcohol dependence in veterans with PTSD. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2012;36:226A.
-
- Batki SL, Lasher BA, Herbst E, Prathikanti S, Metzler T, Tarasovsky G, et al. Topiramate treatment of alcohol dependence in veterans with PTSD: baseline alcohol use and PTSD severity. American Journal on Addictions 2011;21(4):382.
-
- Batki SL, Lasher BA, Metzler T, Heinz AJ, Herbst E, Waldrop A, et al. Predictors of outcome in a pilot controlled trial of topiramate for alcohol dependence in veterans with PTSD. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013:17A. - PubMed
-
- Santos G-M, Lasher BA, Heinz AJ, Kalapatapu R, Herbst E, Metzler T, et al. Urinary ethyl glucuronide and ethyl sulfate testing to evaluate the efficacy of topiramate treatment of alcohol dependence in veterans with PTSD. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37:19A.
Caponi 1985 {published data only}
-
- Caponi A, Realini R, Macciocchi A. A double-blind clinical trial of camazepam vs bromazepam in the treatment of anxio-depressive syndrome in alcoholic patients [Studio doppio cieco camazepam versus bromazepam nel trattamento delle sindromi ansioso-depressive in soggetti etillisti]. Progresso Medico 1985;41(12):731-7.
Ciraulo 2013 {published data only}
Guardia 2012 {published data only}
-
- Guardia J. Clinical trial with ziprasidone for the treatment of psychiatric pathology, not being a severe mental disorder, associated to alcohol dependence. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00197951 (accessed February 2014).
Kranzler 1994 {published data only}
-
- Kranzler HR, Burleson JA, Del Boca FK, Babor TF, Korner P, Brown J, et al. Buspirone treatment of anxious alcoholics. A placebo-controlled trial. Archives of General Psychiatry 1994;51(9):720-31. - PubMed
Krupitsky 1993 {published data only}
-
- Krupitsky EM, Burakov AM, Ivanov VB, Krandashova GF, Lapin IP, Grinenko AJ, et al. Baclofen administration for the treatment of affective disorders in alcoholic patients. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1993;33(2):157-63. - PubMed
Krupitsky 2013 {published data only}
-
- Krupitsky E, Yerish S, Rybakova K, Kiselev A. Single blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial of trazodon for alcoholism comorbid with affective disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37:18A.
Liappas 2003 {published data only}
-
- Liappas J, Paparrigopoulos T, Tzavellas E, Christodoulou G. Alcohol detoxification and social anxiety symptoms: a preliminary study of the impact of mirtazapine administration. Journal of Affective Disorders 2003;76(1-3):279-84. - PubMed
Loo 1986 {published data only}
-
- Loo H, Guelfi JD, Malka R, Brion S, Cottin M, Gailledreau J, et al. Anxiolytic efficacy and tolerance of tetrabamate in anxious patients abusing alcohol. Multicenter double-blind versus placebo study [Efficacité anxiolytique et tolérance du tétrabamate chez des patients anxieux abusant de l'alcool. Etude multicentrique en double insu contre placebo]. Encephale 1986;12(5):291-7. - PubMed
Malcolm 1992 {published data only}
-
- Malcolm R, Anton RF, Randall CL, Johnston A, Brady K, Thevos A. A placebo-controlled trial of buspirone in anxious inpatient alcoholics. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 1992;16(6):1007-13. - PubMed
-
- Moak DH, Anton RF, Malcolm R, Randall CL, Brady K. Alcoholic subjects with anxiety disorder: characteristics of completers and noncompleters in a pharmacologic study. American Journal on Addictions 1993;2(1):39-47.
Oluwadara 2013 {published data only}
-
- Oluwadara BO, Roache JD, Guajardo J, Raj JJ. Correlation pattern of alcohol use and PTSD symptoms among combat veterans in treatment for comorbid PTSD and alcohol use disorder. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37:331A.
-
- Roache JD, Guajardo J, Raj JJ. Preliminary examination of alcoholism subtypes in PTSD and alcohol use dual diagnosis. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2013;37(Suppl 2):331A.
Schadé 2005b {published data only}
-
- Schadé A, Marquenie LA, Balkom AJ, Koeter MM, den Brink W, Dyck R. The effectiveness of anxiety treatment on alcohol-dependent patients with a comorbid phobic disorder: a randomised controlled trial [Effectiviteit van een toegevoegde behandeling voor angstklachten bij alcoholafhankelijke patienten met een fobische stoornis]. Tijdschrift Voor Psychiatrie 2008;50(3):137-48. - PubMed
-
- Schadé A, Marquenie LA, Balkom AJ, Koeter MW, Beurs E, den Brink W, et al. The effectiveness of anxiety treatment on alcohol-dependent patients with a comorbid phobic disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2005;29(5):794-800. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
NCT00248612 {unpublished data only}
-
- Farchione TJ. CBT and venlafaxine treatments for anxiety in alcoholism. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00248612 (accessed August 2013).
NCT00330239 {published data only}
-
- Sonne SC, Brady KT. Paroxetine treatment in outpatients with comorbid PTSD and substance dependence. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00330239 (accessed February 2014).
NCT00352469 {published data only}
-
- Sattar P. 12 week prospective double blind placebo controlled randomized trial of Seroquel SR for alcohol dependence and comorbid anxiety. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00352469 (accessed August 2013).
NCT01408641 {published data only}
-
- Fischer B. A 14-week randomized, placebo-controlled study of topiramate for alcohol use disorders in veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01408641 (accessed February 2014).
NCT01518972 {published data only}
-
- Simpson T. A placebo-controlled trial of prazosin in individuals with co-occurring alcohol dependence and PTSD. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01518972 (accessed February 2014).
Powell 1995 {published data only}
-
- Powell BJ, Campbell JL, Landon JF, Liskow BI, Thomas HM, Nickel EJ, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of nortriptyline and bromocriptine in male alcoholics subtyped by comorbid psychiatric disorders. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 1995;19(2):462-8. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT00585780 {published data only}
-
- Sinha R. Prazosin to reduce stress-induced alcohol/drug craving and relapse. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00585780 (accessed August 2013).
NCT00744055 {published data only}
-
- Ralevski E. The use of prazosin for treatment of patients with alcohol dependence (AD) and post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00744055 (accessed August 2013).
NCT01749215 {published data only}
-
- Batki, SL. A controlled trial of topiramate treatment for alcohol dependence in veterans with PTSD. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01749215 (accessed February 2014).
NCT01847469 {published data only}
-
- Petrakis I. Zonisamide in addition to enhanced cognitive processing therapy-C (E-CPT-C) for veterans with PTSD and comorbid alcohol dependence. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01847469 (accessed February 2014).
Additional references
Alonso 2004
-
- Alonso J, Angermeyer MC, Bernert S, Bruffaerts R, Brugha TS, Bryson H, et al, ESEMeD/MHEDEA 2000 Investigators, European Study of the Epidemiology of Mental Disorders (ESEMeD) Project. 12-Month comorbidity patterns and associated factors in Europe: results from the European Study of the Epidemiology of Mental Disorders (ESEMeD) project. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica Supplementum 2004;420:28-37. - PubMed
Als‐Nielsen 2003
-
- Als-Nielsen B, Chen W, Gluud C, Kjaergard LL. Association of funding and conclusions in randomized drug trials: a reflection of treatment effect or adverse events? Journal of the American Medical Association 2003;290:921-8. - PubMed
Alvanzo 2014
APA 1980
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-III). 3rd edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1980.
APA 1994
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-IV). 4th edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 1994.
APA 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-IV-TR). 4th revised edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
Back 2006
-
- Back SE, Brady KT, Sonne SC, Verduin ML. Symptom improvement in co-occurring PTSD and alcohol dependence. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 2006;194(9):690-6. - PubMed
Baker 2003
-
- Baker CB, Johnsrud MT, Crismon ML, Rosenheck RA, Woods SW. Quantitative analysis of sponsorship bias in economic studies of antidepressants. British Journal of Psychiatry 2003;183:498-506. - PubMed
BAP 2014
-
- Baldwin DS, Anderson IM, Nutt DJ, Allgulander C, Bandelow B, den Boer JA, et al. Evidence-based pharmacological treatment of anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder: a revision of the 2005 guidelines from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2014;28:403-39. - PubMed
Baxter 2014
-
- Baxter AJ, Vos T, Scott KM, Ferrari AJ, Whiteford HA. The global burden of anxiety disorders in 2010. Psychological Medicine 2014;22:1-12. - PubMed
Beck 1961
-
- Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Archives of General Psychiatry 1961;4:561-71. - PubMed
Berenz 2012
Bills 1993
-
- Bills LJ, Kreisler K. Treatment of flashbacks with naltrexone. American Journal of Psychiatry 1993;150(9):1430. - PubMed
Blake 1990
-
- Blake DD, Weathers FW, Nagy LM, Kaloupek DG, Gusman FD, Charney DS, et al. A clinician rating scale for assessing current and lifetime PTSD: the CAPS-1. Behavior Therapy 1990;21:187-8.
Booth 2000
-
- Booth BM, Kirchner J, Fortney J, Ross R, Rost K. Rural at-risk drinkers: correlates and one-year use of alcoholism treatment services. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2000;61:267-77. - PubMed
Boschloo 2013
-
- Boschloo L, Vogelzangs N, den Brink W, Smit JH, Veltman DJ, Beekman ATF, et al. Depressive and anxiety disorders predicting first incidence of alcohol use disorders: results of the Netherlands Study of Depression and Anxiety (NESDA). Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2013;74:1233-40. - PubMed
Bowen 2000
-
- Bowen RC, D'Arcy C, Keegan D, Senthilselvan A. A controlled trial of cognitive behavioral treatment of panic in alcoholic inpatients with comorbid panic disorder. Addictive Behaviors 2000;25(4):593-7. - PubMed
Brady 1993
-
- Brady KT, Lydiard RB. The association of alcoholism and anxiety. Psychiatric Quarterly 1993;64(2):135-49. - PubMed
Brookwell 2014
-
- Brookwell L, Hogan C, Healy D, Mangin D. Ninety-three cases of alcohol dependence following SSRI treatment. International Journal of Risk & Safety in Medicine 2014;26:99-107. - PubMed
Bühler 2011
-
- Bühler M, Mann K. Alcohol and the human brain: a systematic review of different neuroimaging methods. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2011;35:1771-93. - PubMed
Cohen 2007
-
- Cohen E, Feinn R, Arias A, Kranzler HR. Alcohol treatment utilization: findings from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2007;86:214-21. - PubMed
Connor 2000
-
- Connor KM, Davidson JR, Churchill LE, Sherwood A, Foa E, Weisler RH. Psychometric properties of the Social Phobia Inventory (SPIN). New self-rating scale. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:379-86. - PubMed
CPA 2006
-
- Canadian Psychiatric Association. Clinical practice guidelines. Management of anxiety disorders. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 2006;51(8 Suppl 2):9S-91S. - PubMed
Dawson 2012
Dawson 2013
Deeks 2002
-
- Deeks JJ. Issues in the selection of a summary statistic for meta-analysis of clinical trials with binary outcomes. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(11):1575-600. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks J, Higgins J, Altman D. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Dickersin 1992
-
- Dickersin K, Min YI, Meinert CL. Factors influencing the publication of research results: follow-up of applications submitted to two substantial review boards. JAMA 1992;267(3):374-8. - PubMed
Driessen 2001
-
- Driessen M, Meier S, Hill A, Wetterling T, Lange W, Junghanns K. The course of anxiety, depression and drinking behaviours after completed detoxification in alcoholics with and without comorbid anxiety and depressive disorders. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2001;36(3):249-55. - PubMed
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne DR, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtin F, Worthington HV, Vail A. Meta-analyses involving cross-over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140-9. - PubMed
Feltner 2003
-
- Feltner DE, Crockatt JG, Dubovsky SJ, Cohn CK, Shrivastava RK, Targum SD, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose, multi-center study of pregabalin in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2003;23(3):240-9. - PubMed
Gahr 2013
-
- Gahr M, Franke B, Freudenmann RW, Kölle MA, Schönfeldt-Lecuona C. Concerns about pregabalin: further experience with its potential of causing addictive behaviors. Journal of Addiction Medicine 2013;7:147-9. - PubMed
Guy 1976
-
- Guy W. ECDEU assessment manual for psychopharmacology. Washington, DC: U.S. National Institute of Health, 1976.
Hamilton 1959
-
- Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. British Journal of Medical Psychology 1959;32:50-5. - PubMed
Hamilton 1969
-
- Hamilton M. Standardised assessment and recording of depressive symptoms. Psychiatria, Neurologia, Neurochirurgia 1969;72:201-5. - PubMed
Hasin 2003
Hasin 2007
-
- Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF. Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Archives of General Psychiatry 2007;64(7):830-42. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Hoertel 2012
-
- Hoertel N, Le Strat Y, Blanco C, Lavaud P, Dubertret C. Generalizability of clinical trial results for generalized anxiety disorder to community samples. Depression and Anxiety 2012;29:614-20. - PubMed
Hofmann 2013
Hopewell 2009
Horowitz 1979
-
- Horowitz M, Wilner N, Alvarez W. Impact of Event Scale: a measure of subjective stress. Psychosomatic Medicine 1979;41(3):209-18. - PubMed
Johnson 2003
-
- Johnson BA, Ait-Daoud N, Ma JZ, Wang Y. Ondansetron reduces mood disturbance among biologically predisposed, alcohol-dependent individuals. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2003;27(11):1773-9. - PubMed
Keane 1988
-
- Keane TM, Caddell JM, Taylor KL. Mississippi Scale for Combat-Related Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: three studies in reliability and validity. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1988;56(1):85-90. - PubMed
Kendall 2004
-
- Kendall PC, Safford S, Flannery-Schroeder E, Webb A. Child anxiety treatment: outcomes in adolescence and impact on substance use and depression at 7.4-year follow-up. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2004;72(2):276-87. - PubMed
Kessler 1996
-
- Kessler RC, Nelson CB, McGonagle KA, Edlund MJ, Frank RG, Leaf PJ. The epidemiology of co-occurring addictive and mental disorders: implications for prevention and service utilization. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 1996;66(1):17-31. - PubMed
Kessler 1997
-
- Kessler RC, Crum RM, Warner LA, Nelson CB, Schulenberg J, Anthony JC. Lifetime co-occurrence of DSM-III-R alcohol abuse and dependence with other psychiatric disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey. Archives of General Psychiatry 1997;54(4):313-21. - PubMed
Khantzian 1985
-
- Khantzian EJ. The self-medication hypothesis of addictive disorders: focus on heroin and cocaine dependence. American Journal of Psychiatry 1985;142(11):1259-64. - PubMed
Koen 2011
Kranzler 2006
-
- Kranzler HR, Burleson JA, Brown J, Babor TF. Fluoxetine treatment seems to reduce the beneficial effects of cognitive-behavioral therapy in type B alcoholics. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2006;20(9):1534-41. - PubMed
Kranzler 2012
Krystal 2006
-
- Krystal JH, Staley J, Mason G, Petrakis IL, Kaufman J, Harris RA, et al. Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors and alcoholism: intoxication, dependence, vulnerability, and treatment. Archives of General Psychiatry 2006;63(9):957-68. - PubMed
Kushner 1990
-
- Kushner MG, Sher KJ, Beitman BD. The relation between alcohol problems and the anxiety disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry 1990;147(6):685-95. - PubMed
Kushner 2005
-
- Kushner MG, Abrams K, Thuras P, Hanson KL, Brekke M, Sletten S. Follow-up study of anxiety disorder and alcohol dependence in comorbid alcoholism treatment patients. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2005;29(8):1432-43. - PubMed
Kwo 1998
-
- Kwo PY, Ramchandani VA, O'Connor S, Amann D, Carr LG, Sandrasegaran K, et al. Gender differences in alcohol metabolism: relationship to liver volume and effect of adjusting for body mass. Gastroenterology 1998;115:1552-7. - PubMed
Lev‐Ran 2012
-
- Lev-Ran S, Balchand K, Lefebvre L, Araki KF, Le Foll B. Pharmacotherapy of alcohol use disorders and concurrent psychiatric disorders: a review. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry 2012;57(6):342-9. - PubMed
Liappas 2005
-
- Liappas J, Paparrigopoulos T, Tzavellas E, Rabavilas A. Mirtazapine and venlafaxine in the management of collateral psychopathology during alcohol detoxification. Progress in Neuro-psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry 2005;29:55-60. - PubMed
Liebowitz 1987
-
- Liebowitz MR. Social phobia. Modern Problems in Pharmacopsychiatry 1987;22:141-73. - PubMed
Lubin 2002
-
- Lubin G, Weizman A, Shmushkevitz M, Valevski A. Short-term treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder with naltrexone: an open-label preliminary study. Human Psychopharmacology 2002;17(4):181-5. - PubMed
Lumley 2002
-
- Lumley T. Network meta-analysis for indirect treatment comparisons. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21(16):2313-24. - PubMed
Malcolm 2002
Marshall 2001
-
- Marshall RD, Beebe KL, Oldham M, Zaninelli R. Efficacy and safety of paroxetine treatment for chronic PTSD: a fixed-dose, placebo-controlled study. American Journal of Psychiatry 2001;158(12):1982-8. - PubMed
Marshall 2007
-
- Marshall RD, Lewis-Fernandez R, Blanco C, Simpson HB, Lin SH, Vermes D, et al. A controlled trial of paroxetine for chronic PTSD, dissociation, and interpersonal problems in mostly minority adults. Depression and Anxiety 2007;24(2):77-84. - PubMed
McLean 2011
McLellan 1990
-
- McLellan AT, Parikh G, Bragg A, Cacciola J, Fureman B, Incmikoski R. Addiction Severity Index: Administration Manual. 5th edition. Philadelphia: Pennsylvania Veterans' Administration Center for Studies of Addiction, 1990.
Montgomery 1979
-
- Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. British Journal of Psychiatry 1979;134:382-9. - PubMed
Morris 2005
-
- Morris EP, Stewart SH, Ham LS. The relationship between social anxiety disorder and alcohol use disorders: a critical review. Clinical Psychology Review 2005;25(6):734-60. - PubMed
Mukherjee 2008
-
- Mukherjee S, Das SK, Vaidyanathan K, Vasudevan, DM. Consequences of alcohol consumption on neurotransmitters - an overview. Current Neurovascular Research 2008;5(4):266-72. - PubMed
NICE 2005
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Clinical Guideline 31. Obsessive-compulsive disorder: core interventions in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder and body dysmorphic disorder, 2005. www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg031 (accessed 30 December 2014). - PubMed
Oakman 2003
-
- Oakman J, Van Ameringen M, Mancini C, Farvolden P. A confirmatory factor analysis of a self-report version of the Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology 2003;59:149-61. - PubMed
Pande 2004
-
- Pande AC, Feltner DE, Jefferson JW, Davidson JRT, Pollack M, Stein MB, et al. Efficacy of the novel anxiolytic pregabalin in social anxiety disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2004;24(2):141-9. - PubMed
Papazisis 2013
-
- Papazisis G, Garyfallos G, Sardeli C, Kouvelas D. Pregabalin abuse after past substance-seeking behavior. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2013;51:441-2. - PubMed
Petrakis 2006
-
- Petrakis IL, Poling J, Levinson C, Nich C, Carroll K, Ralevski E, et al. Naltrexone and disulfiram in patients with alcohol dependence and comorbid post-traumatic stress disorder. Biological Psychiatry 2006;60(7):777-83. - PubMed
Pettinati 2000
-
- Pettinati HM, Volpicelli JR, Kranzler HR, Luck G, Rukstalis MR, Cnaan A. Sertraline treatment for alcohol dependence: interactive effects of medication and alcoholic subtype. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2000;24(7):1041-9. - PubMed
Pohl 2005
-
- Pohl RB, Feltner DE, Fieve RR, Pande AC. Efficacy of pregabalin in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: double-blind, placebo-controlled comparison of BID versus TID dosing. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2005;25(2):151-8. - PubMed
Project MATCH 1993
-
- Project MATCH . Project MATCH (Matching Alcoholism Treatment to Client Heterogeneity): rationale and methods for a multisite clinical trial matching patients to alcoholism treatment. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 1993;17(6):1130-45. - PubMed
Randall 2001a
-
- Randall CL, Thomas S, Thevos AK. Concurrent alcoholism and social anxiety disorder: a first step toward developing effective treatments. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2001;25(2):210-20. - PubMed
Regier 1990
-
- Regier DA, Farmer ME, Rae DS, Locke BZ, Keith SJ, Judd LL, et al. Comorbidity of mental disorders with alcohol and other drug abuse. Results from the Epidemiologic Catchment Area (ECA) Study. JAMA 1990;264(19):2511-8. - PubMed
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Rickels 2005
-
- Rickels K, Pollack MH, Feltner DE, Lydiard RB, Zimbroff DL, Bielski RJ, et al. Pregabalin for treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: a 4-week, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of pregabalin and alprazolam. Archives of General Psychiatry 2005;62(9):1022-30. - PubMed
Roberts 2012
Robinson 2002
-
- Robinson KA, Dickersin K. Development of a highly sensitive search strategy for the retrieval of reports of controlled trials using PubMed. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31:150-3. - PubMed
Schadé 2003
-
- Schadé A, Marquenie LA, Van Balkom AJ, De Beurs E, Van Dyck R, Van Den Brink W. Do comorbid anxiety disorders in alcohol-dependent patients need specific treatment to prevent relapse? Alcohol and Alcoholism 2003;38(3):255-62. - PubMed
Schadé 2005a
-
- Schadé A, Marquenie LA, Balkom AJ, Koeter MW, Beurs E, den Brink W, et al. The effectiveness of anxiety treatment on alcohol-dependent patients with a comorbid phobic disorder: a randomized controlled trial. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2005;29(5):794-800. - PubMed
Schuckit 1988
-
- Schuckit MA, Monteiro MG. Alcoholism, anxiety and depression. British Journal of Addiction 1988;83(12):1373-80. - PubMed
Schwan 2010
-
- Schwan S, Sundström A, Stjernberg E, Hallberg E, Hallberg P. A signal for an abuse liability for pregabalin - results from the Swedish spontaneous adverse drug reaction reporting system. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2010;66:947-53. - PubMed
Schweizer 1986
-
- Schweizer E, Rickels K, Lucki I. Resistance to the anti-anxiety effect of buspirone in patients with a history of benzodiazepine use. New England Journal of Medicine 1986;314:719-20. - PubMed
Shah 2001
-
- Shah R, Uren Z, Baker A, Majeed A. Deaths from antidepressants in England and Wales 1993-1997: analysis of a new national database. Psychological Medicine 2001;31:1203-10. - PubMed
Shear 1997
-
- Shear MK, Brown TA, Barlow DH, Money R, Sholomskas DE, Woods SW, et al. Multicenter collaborative Panic Disorder Severity Scale. American Journal of Psychiatry 1997;154:1571-5. - PubMed
Sheehan 1996
-
- Sheehan DV, Harnett-Sheehan K, Raj BA. The measurement of disability. International Clinical Psychopharmacology 1996;11 Suppl 3:89-95. - PubMed
Smith 2012
Sobell 1992
-
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB. Timeline Follow-Back: a technique for assessing self-reported ethanol consumption. In: Allen J, Litten RZ, editors(s). Measuring Alcohol Consumption: Psychological and Biological Methods. Totowa: Humana Press, 1992:41-72.
Sofuoglu 2014
Song 2000
-
- Song F, Eastwood AJ, Gilbody S, Duley L, Sutton AJ. Publication and related biases. Health Technology Assessment 2000;4(10):1-115. - PubMed
Spitzer 1996
-
- Spitzer R, Williams J, Gibbons M. Instructional Manual for the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV. New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute, 1996.
Stein 2009
-
- Stein DJ, Ipser J, McAnda N. Pharmacotherapy of posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of meta-analyses and treatment guidelines. CNS Spectrums 2009;14(1 Suppl 1):25-30. - PubMed
Stewart 2008
-
- Stewart SH, Conrod PJ. Anxiety disorder and substance use disorder co-morbidity: common themes and future directions. In: Anxiety and Substance Use Disorders: the Vicious Cycle of Comorbidity. Series in Anxiety and Related Disorders. New York: Springer, 2008:239-57.
Thomas 2008
-
- Thomas SE, Randall PK, Book SW, Randall CL. A complex relationship between co-occurring social anxiety and alcohol use disorders: what effect does treating social anxiety have on drinking? Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32(1):77-84. - PubMed
Torrens 2005
-
- Torrens M, Fonseca F, Mateu G, Farré M. Efficacy of antidepressants in substance use disorders with and without comorbid depression. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2005;78(1):1-22. - PubMed
Tucker 2001
-
- Tucker P, Zaninelli R, Yehuda R, Ruggiero L, Dillingham K, Pitts CD. Paroxetine in the treatment of chronic posttraumatic stress disorder: results of a placebo-controlled, flexible-dosage trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2001;62(11):860-8. - PubMed
Tucker 2007
-
- Tucker P, Trautman RP, Wyatt DB, Thompson J, Wu SC, Capece JA, et al. Efficacy and safety of topiramate monotherapy in civilian posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2007;68:201-20. - PubMed
Ugochukwu 2013
-
- Ugochukwu C, Bagot KS, Delaloye S, Pi S, Vien L, Garvey T, et al. The importance of quality of life in patients with alcohol abuse and dependence. Harvard Review of Psychiatry 2013;21:1-17. - PubMed
Verbeke 2000
-
- Verbeke M, Molenberghs G. Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data. New York: Springer, 2000.
Vesga‐López 2008
Ware 1992
-
- Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item Short-Form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Medical Care 1992;30(6):473-83. - PubMed
Watkins 2005
-
- Watkins KE, Hunter SB, Burnam MA, Pincus HA, Nicholson G. Review of treatment recommendations for persons with a co-occurring affective or anxiety and substance use disorder. Psychiatric Services 2005;56(8):913-26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

