metaSEM: an R package for meta-analysis using structural equation modeling
- PMID: 25601849
- PMCID: PMC4283449
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2014.01521
metaSEM: an R package for meta-analysis using structural equation modeling
Abstract
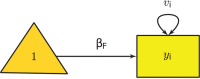
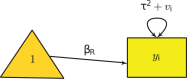
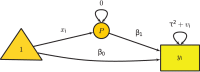
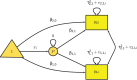
The metaSEM package provides functions to conduct univariate, multivariate, and three-level meta-analyses using a structural equation modeling (SEM) approach via the OpenMx package in the R statistical platform. It also implements the two-stage SEM approach to conducting fixed- and random-effects meta-analytic SEM on correlation or covariance matrices. This paper briefly outlines the theories and their implementations. It provides a summary on how meta-analyses can be formulated as structural equation models. The paper closes with a conclusion on several relevant topics to this SEM-based meta-analysis. Several examples are used to illustrate the procedures in the supplementary material.
Keywords: R; meta-analysis; meta-analytic structural equation modeling; metaSEM; structural equation modeling.
Figures
References
-
- Arthur W., Bennett W., Huffcutt A. I. (2001). Conducting Meta-Analysis using SAS. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
-
- Becker B. J. (2009). Model-based meta-analysis, in The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis, 2nd Edn., eds Cooper H., Hedges L. V., Valentine J. C. (New York, NY: Russell Sage Foundation; ), 377–395.
-
- Borenstein M., Hedges L. V., Rothstein H. R. (2005). Comprehensive Meta-Analysis, Version 2. Englewood, NJ: Biostat, Inc.
-
- Borenstein M., Hedges L. V., Higgins J. P., Rothstein H. R. (2009). Introduction to Meta-Analysis. Chichester; Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons; 10.1002/9780470743386 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources