Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in the Monitoring of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review
- PMID: 25603012
- PMCID: PMC4492772
- DOI: 10.1089/neu.2014.3748
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in the Monitoring of Adult Traumatic Brain Injury: A Review
Abstract
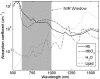
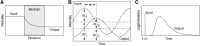
Cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) has long represented an exciting prospect for the noninvasive monitoring of cerebral tissue oxygenation and perfusion in the context of traumatic brain injury (TBI), although uncertainty still exists regarding the reliability of this technology specifically within this field. We have undertaken a review of the existing literature relating to the application of NIRS within TBI. We discuss current "state-of-the-art" NIRS monitoring, provide a brief background of the technology, and discuss the evidence regarding the ability of NIRS to substitute for established invasive monitoring in TBI.
Keywords: brain; injury; near-infrared; review; spectroscopy; trauma.
Figures
References
-
- Hodgkinson S., Pollit V., Sharpin C., and Lecky F. (2014). Early management of head injury: summary of updated NICE guidance. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 348, g104 - PubMed
-
- Ghosh A., Elwell C., and Smith M. (2012). Review article: cerebral near-infrared spectroscopy in adults: a work in progress. Anesth. Analg. 115, 1373–1383 - PubMed
-
- Jobsis F.F. (1977). Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science 198, 1264–1267 - PubMed
-
- Ferrari M., Giannini I., Sideri G., and Zanette E. (1985). Continuous non invasive monitoring of human brain by near infrared spectroscopy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 191, 873–882 - PubMed
-
- Boushel R., Langberg H., Olesen J., Gonzales–Alonzo J., Bulow J., and Kjaer M. (2001). Monitoring tissue oxygen availability with near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in health and disease. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 11, 213–222 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

