Catalase inhibits ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
- PMID: 25603016
- PMCID: PMC4440990
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2014.0402
Catalase inhibits ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells
Abstract
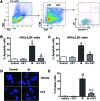
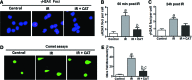
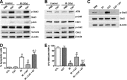
Hematologic toxicity is a major cause of mortality in radiation emergency scenarios and a primary side effect concern in patients undergoing chemo-radiotherapy. Therefore, there is a critical need for the development of novel and more effective approaches to manage this side effect. Catalase is a potent antioxidant enzyme that coverts hydrogen peroxide into hydrogen and water. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of catalase as a protectant against ionizing radiation (IR)-induced toxicity in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). The results revealed that catalase treatment markedly inhibits IR-induced apoptosis in murine hematopoietic stem cells and hematopoietic progenitor cells. Subsequent colony-forming cell and cobble-stone area-forming cell assays showed that catalase-treated HSPCs can not only survive irradiation-induced apoptosis but also have higher clonogenic capacity, compared with vehicle-treated cells. Moreover, transplantation of catalase-treated irradiated HSPCs results in high levels of multi-lineage and long-term engraftments, whereas vehicle-treated irradiated HSPCs exhibit very limited hematopoiesis reconstituting capacity. Mechanistically, catalase treatment attenuates IR-induced DNA double-strand breaks and inhibits reactive oxygen species. Unexpectedly, we found that the radioprotective effect of catalase is associated with activation of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway and pharmacological inhibition of STAT3 abolishes the protective activity of catalase, suggesting that catalase may protect HSPCs against IR-induced toxicity via promoting STAT3 activation. Collectively, these results demonstrate a previously unrecognized mechanism by which catalase inhibits IR-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in HSPCs.
Figures



References
-
- Mauch P, Constine L, Greenberger J, Knospe W, Sullivan J, Liesveld JL. and Deeg HJ. (1995). Hematopoietic stem cell compartment: acute and late effects of radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1319–1339 - PubMed
-
- Daniel D. and Crawford J. (2006). Myelotoxicity from chemotherapy. Semin Oncol 33:74–85 - PubMed
-
- Meng A, Wang Y, Brown SA, Van Zant G. and Zhou D. (2003). Ionizing radiation and busulfan inhibit murine bone marrow cell hematopoietic function via apoptosis dependent and independent mechanisms. Exp Hematol 31:1348–1356 - PubMed
-
- Coleman CN, Stone HB, Moulder JE. and Pellmar TC. (2004). Modulation of radiation injury. Science 304:693–694 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

