BRD4 inhibitor inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis
- PMID: 25603177
- PMCID: PMC4307342
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms16011928
BRD4 inhibitor inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis
Abstract
Post-translational modifications have been identified to be of great importance in cancers and lysine acetylation, which can attract the multifunctional transcription factor BRD4, has been identified as a potential therapeutic target. In this paper, we identify that BRD4 has an important role in colorectal cancer; and that its inhibition substantially wipes out tumor cells. Treatment with inhibitor MS417 potently affects cancer cells, although such effects were not always outright necrosis or apoptosis. We report that BRD4 inhibition also limits distal metastasis by regulating several key proteins in the progression of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This effect of BRD4 inhibitor is demonstrated via liver metastasis in animal model as well as migration and invasion experiments in vitro. Together, our results demonstrate a new application of BRD4 inhibitor that may be of clinical use by virtue of its ability to limit metastasis while also being tumorcidal.
Figures
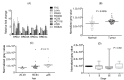
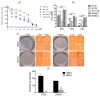

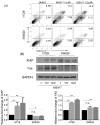

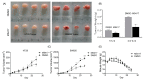


References
-
- Klajic J., Busato F., Edvardsen H., Touleimat N., Fleischer T., Bukholm I.R., Borresen-Dale A.L., Lonning P.E., Tost J., Kristensen V.N. DNA Methylation Status of Key Cell Cycle Regulators such as CDKNA2/p16 and CCNA1 Correlates with Treatment Response to Doxorubicin and 5-Fluorouracil in Locally Advanced Breast Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014;20:6357–6366. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0297. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

