Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 25603545
- PMCID: PMC11115378
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007356.pub2
Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rituximab is a selective, B-cell depleting, biologic agent for treating refractory rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeted against CD 20 that is promoted as therapy for patients who fail to respond to other biologics. There is evidence to suggest that rituximab is effective and well tolerated when used in combination with methotrexate for RA.
Objectives: To evaluate the benefits and harms of rituximab for the treatment of RA.
Search methods: We conducted a search (until January 2014) in electronic databases (The Cochrane Library, MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, Web of Science), clinical trials registries, and websites of regulatory agencies. Reference lists from comprehensive reviews were also screened.
Selection criteria: All controlled trials comparing treatment with rituximab as monotherapy or in combination with any disease modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) (traditional or biologic) versus placebo or other DMARD (traditional or biologic) in adult patients with active RA.
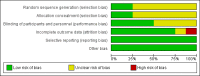
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently assessed the risk of bias and abstracted data from each study.
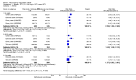
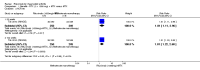
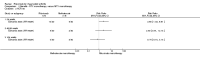
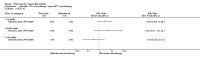
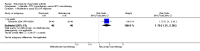
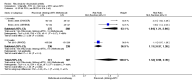
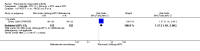
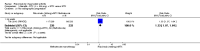
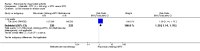
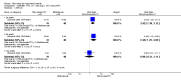
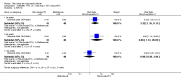
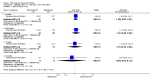
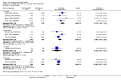
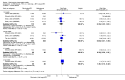
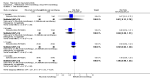
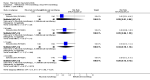
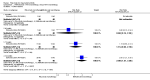
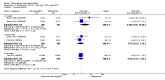
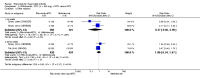
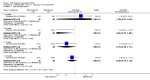
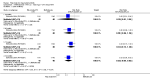
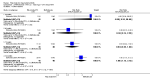
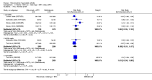
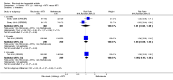
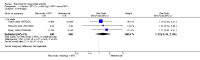
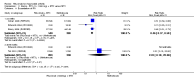
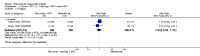
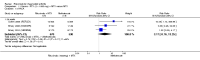
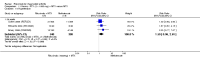
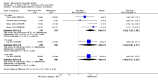
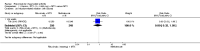
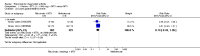
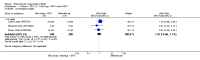
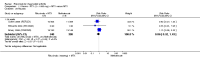
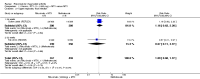
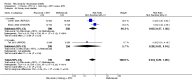
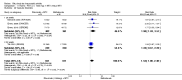
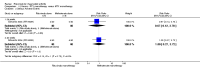
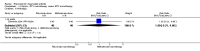
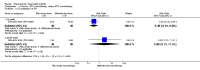
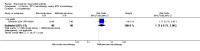
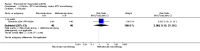
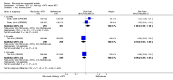
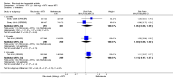
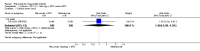
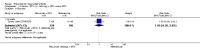
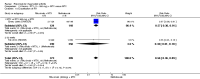
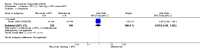
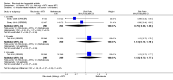
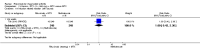
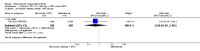
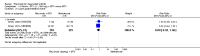
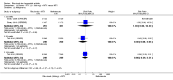
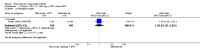
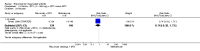
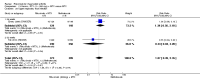
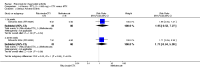
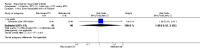
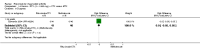
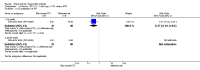
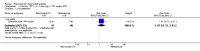
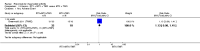
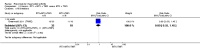
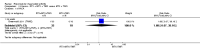
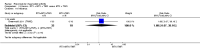
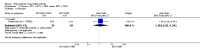
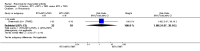
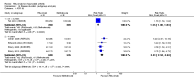
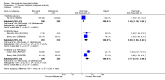
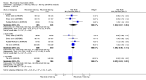
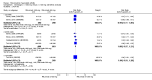
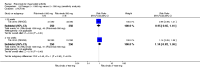
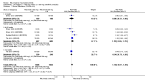
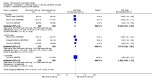
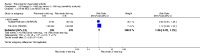
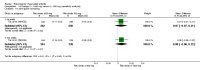
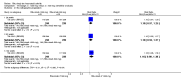
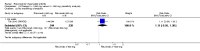
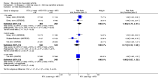
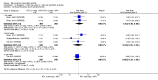
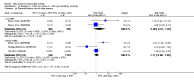
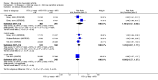
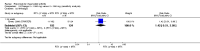
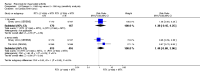
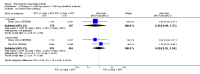
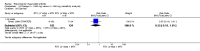
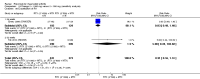
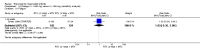
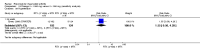
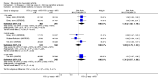
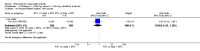
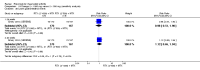
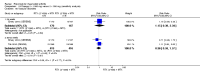
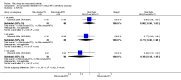
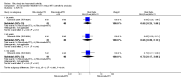
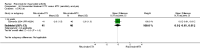
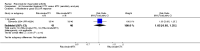
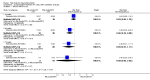
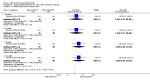
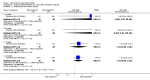
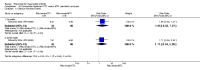
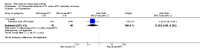
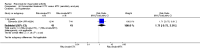
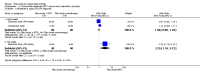
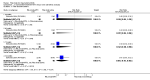
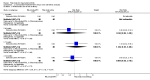
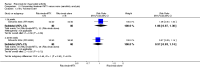
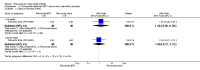
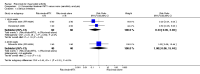
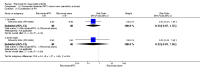
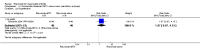
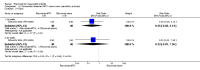
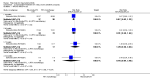
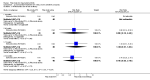
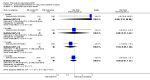
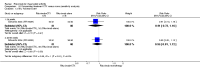
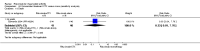
Main results: We included eight studies with 2720 patients. For six studies selection bias could not be evaluated and two studies were considered to have low risk of bias. The level of evidence ranged from low to high, but was rated as moderate for most outcomes. We have prioritised reporting of rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate since this is the approved dose and most commonly used combination. We also reported data on other combinations and doses as supplementary information in the results section of the review.American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50 response rates were statistically significantly improved with rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate compared with methotrexate alone at 24 to 104 weeks. The RR for achieving an ACR 50 at 24 weeks was 3.3 (95% CI 2.3 to 4.6); 29% of patients receiving rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate achieved the ACR 50 compared to 9% of controls. The absolute treatment benefit (ATB) was 21% (95% CI 16% to 25%) with a number needed to treat (NNT) of 6 (95% CI 4 to 9).At 52 weeks, the RR for achieving clinical remission (Disease Activity Score (DAS) 28 joints < 2.6) with rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate compared with methotrexate monotherapy was 2.4 (95% CI 1.7 to 3.5); 22% of patients receiving rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate achieved clinical remission compared to 11% of controls. The ATB was 11% (95% CI 2% to 20%) with a NNT of 7 (95% CI 4 to 13).At 24 weeks, the RR for achieving a clinically meaningful improvement (CMI) in the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) (> 0.22) for patients receiving rituximab combined with methotrexate compared to patients on methotrexate alone was 1.6 (95% CI 1.2 to 2.1). The ATB was 24% (95% CI 12% to 36%) with an NNT of 5 (95% CI 3 to 13). At 104 weeks, the RR for achieving a CMI in HAQ (> 0.22) was 1.4 (95% CI 1.3 to 1.6). The ATB was 24% (95% CI 16% to 31%) with a NNT of 5 (95% CI 3 to 7).At 24 weeks, the RR for preventing radiographic progression in patients receiving rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate was 1.2 (95% CI 1.0 to 1.4) compared to methotrexate alone; 70% of patients receiving rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate had no radiographic progression compared to 59% of controls. The ATB was 11% (95% CI 2% to 19%) and the NNT was 10 (95% CI 5 to 57). Similar benefits were observed at 52 to 56 weeks and 104 weeks.Statistically significantly more patients achieved a CMI on the physical and mental components of the quality of life, measured by the Short Form (SF)-36, in the rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate-treated group compared with methotrexate alone at 24 to 52 weeks (RR 2.0, 95% CI 1.1 to 3.4; NNT 4, 95% CI 3 to 8 and RR 1.4, 95% CI 1.1 to 1.9; NNT 8, 95% CI 5 to 19, respectively); 34 and 13 more patients out of 100 showed an improvement in the physical component of the quality of life measure compared to methotrexate alone (95% CI 5% to 84%; 95% CI 7% to 8%, respectively).There was no evidence of a statistically significant difference in the rates of withdrawals because of adverse events or for other reasons (that is, withdrawal of consent, violation, administrative, failure to return) in either group. However, statistically significantly more people receiving the control drug withdrew from the study compared to those receiving rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate at all times (RR 0.40, 95% CI 0.32 to 0.50; RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.91; RR 0.48, 95% CI 0.28 to 0.82; RR 0.58, 95% CI 0.45 to 0.75, respectively). At 104 weeks, 37% withdrew from the control group and 20% withdrew from the rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate group. The absolute risk difference (ARD) was -20% (95% CI -34% to -5%) with a number needed to harm (NNH) of 7 (95% CI 5 to 11).A greater proportion of patients receiving rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate developed adverse events after their first infusion compared to those receiving methotrexate monotherapy and placebo infusions (RR 1.6, 95% CI 1.3 to 1.9); 26% of those taking rituximab plus methotrexate reported more events associated with their first infusion compared to 16% of those on the control regimen with an ARD of 9% (95% CI 5% to 13%) and a NNH of 11 (95% CI 21 to 8). However, no statistically significant differences were noted in the rates of serious adverse events.
Authors' conclusions: Evidence from eight studies suggests that rituximab (two 1000 mg doses) in combination with methotrexate is significantly more efficacious than methotrexate alone for improving the symptoms of RA and preventing disease progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Suarez‐Almazor is the recipient of a K24 career award from the National Institute for Musculoskeletal and Skin Disorders.
Figures



















































































































































































































Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: In rheumatoid arthritis, adding rituximab to methotrexate improves clinical outcomes.Ann Intern Med. 2015 Jun 16;162(12):JC9. doi: 10.7326/ACPJC-2015-162-12-009. Ann Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26075786 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Cohen 2006 (REFLEX) {published data only}
-
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, et al. REFLEX Trial Group. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti‐tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty‐four weeks. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;54(9):2793‐806. [16947627] - PubMed
-
- Keystone E, Burmester GR, Furie R, Loveless JE, Emery P, Kremer J, et al. Improvement in patient‐reported outcomes in a rituximab trial in patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti‐tumor necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2008;59(6):785‐93. [PUBMED: 18512710] - PubMed
-
- Keystone E, Emery P, Peterfy CG, Tak PP, Cohen S, Genovese MC, et al. Rituximab inhibits structural joint damage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitor therapies. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2009;68(2):216‐21. [PUBMED: 18388156] - PubMed
Edwards 2004 (WA16291) {published data only}
-
- Breedveld F, Agarwal S, Yin M, Ren S, Li NF, Shaw TM, Davies BE. Rituximab pharmacokinetics in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: B‐cell levels do not correlate with clinical response. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2007;47(9):1119‐28. [PUBMED: 17068064] - PubMed
-
- Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz‐Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. Efficacy of B‐cell‐targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine 2004;350(25):2572‐81. [PUBMED: 15201414] - PubMed
-
- Strand V, Balbir‐Gurman A, Pavelka K, Emery P, Li N, Yin M, et al. Sustained benefit in rheumatoid arthritis following one course of rituximab: improvements in physical function over 2 years. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2006;45(12):1505‐13. [PUBMED: 17062648] - PubMed
Emery 2006 (DANCER) {published data only}
-
- Emery P, Fleischmann R, Filipowicz‐Sosnowska A, Schechtman J, Szczepanski L, Kavanaugh A, et al. DANCER Study Group. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: results of a phase IIB randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, dose‐ranging trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;54(5):1390‐400. [PUBMED: 16649186] - PubMed
-
- Mease PJ, Revicki DA, Szechinski J, Greenwald M, Kivitz A, Barile‐Fabris L, et al. Improved health‐related quality of life for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis receiving rituximab: Results of the Dose‐Ranging Assessment: International Clinical Evaluation of Rituximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis (DANCER) Trial. The Journal of Rheumatology 2008;35(1):20‐30. [PUBMED: 18050385] - PubMed
Emery 2010 (SERENE) {published data only}
-
- Emery P, Deodhar A, Rigby WF, Isaacs JD, Combe B, Racewicz AJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of different doses and retreatment of rituximab: a randomised, placebo‐controlled trial in patients who are biological naive with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate (Study Evaluating Rituximab's Efficacy in MTX iNadequate rEsponders (SERENE)). Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(9):1629‐35. [PUBMED: 20488885] - PMC - PubMed
Greenwald 2011 (TAME) {published data only}
-
- Greenwald MW, Shergy WJ, Kaine JL, Sweetser MT, Gilder K, Linnik MD. Evaluation of the safety of rituximab in combination with a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor and methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results from a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2011;63(3):622‐32. [PUBMED: 21360491] - PubMed
Owczarczyk 2008 {published data only}
-
- Owczarczyk K, Hellmann M, Fliedner G, Röhrs T, Maizus K, Passon D, et al. Clinical outcome and B cell depletion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving rituximab monotherapy in comparison with patients receiving concomitant methotrexate. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2008;67(11):1648‐9. [PUBMED: 18854518] - PubMed
Rubbert‐Roth2010 (MIRROR) {published data only}
-
- Rubbert‐Roth A, Tak PP, Zerbini C, Tremblay JL, Carreño L, Armstrong G, et al. MIRROR Trial Investigators. Efficacy and safety of various repeat treatment dosing regimens of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: results of a Phase III randomized study (MIRROR). Rheumatology (Oxford) 2010;49(9):1683‐93. [PUBMED: 20463186] - PMC - PubMed
Tak 2010 (IMAGE) {published data only}
-
- Tak PP, Rigby W, Rubbert‐Roth A, Peterfy C, Vollenhoven RF, Stohl W, et al. Sustained inhibition of progressive joint damage with rituximab plus methotrexate in early active rheumatoid arthritis: 2‐year results from the randomised controlled trial IMAGE. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2012;71(3):351‐7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tak PP, Rigby WF, Rubbert‐Roth A, Peterfy CG, Vollenhoven RF, Stohl W, et al. IMAGE Investigators. Inhibition of joint damage and improved clinical outcomes with rituximab plus methotrexate in early active rheumatoid arthritis: the IMAGE trial. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2011;70(1):39‐46. [PUBMED: 20937671] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Assous 2008 {published data only}
-
- Assous N, Gossec L, Dieudé P, Meyer O, Dougados M, Kahan A, Allanore Y. Rituximab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis in daily practice. The Joural of Rheumatology 2008;35(1):31‐4. - PubMed
Bingham 2010 (SIERRA) {published data only}
-
- Bingham CO 3rd, Looney RJ, Deodhar A, Halsey N, Greenwald M, Codding C, et al. Immunization responses in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with rituximab: results from a controlled clinical trial. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2010;62(1):64‐74. [PUBMED: 20039397] - PubMed
Bokarewa 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bokarewa M, Lindholm C, Zendjanchi K, Nadali M, Tarkowski A. Efficacy of anti‐CD20 treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis resistant to a combination of methotrexate/anti‐TNF therapy. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 2007;66(4):476‐83. - PubMed
Galarza 2008 {published data only}
-
- Galarza C, Valencia D, Tobón GJ, Zurita L, Mantilla RD, Pineda‐Tamayo R, et al. Should rituximab be considered as the first‐choice treatment for severe autoimmune rheumatic diseases?. Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology 2008;34(1):124‐8. - PubMed
Haraoui 2011 (RESET) {published data only}
-
- Haraoui B, Bokarewa M, Kallmeyer I, Bykerk VP, RESET Investigators. Safety and effectiveness of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis following an inadequate response to 1 prior tumor necrosis factor inhibitor: the RESET Trial. The Journal of Rheumatology 2011;38(12):2548‐56. [PUBMED: 21965646] - PubMed
Kavanaugh 2008 (ARISE) {published data only}
Keystone 2007 {published data only}
-
- Keystone E, Fleischmann R, Emery P, Furst DE, Vollenhoven R, Bathon J, et al. Safety and efficacy of additional courses of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: an open‐label extension analysis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2007;56(12):3896‐908. - PubMed
Mease 2010 (SUNRISE) {published data only}
-
- Mease PJ, Cohen S, Gaylis NB, Chubick A, Kaell AT, Greenwald M, et al. Efficacy and safety of retreatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with previous inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: results from the SUNRISE trial. The Journal of Rheumatology 2010;37(5):917‐27. [PUBMED: 20194448] - PubMed
Ng 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ng CM, Bruno R, Combs D, Davies. Population pharmacokinetics of rituximab (anti‐CD20 monoclonal antibody) in rheumatoid arthritis patients during a phase II clinical trial. The Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2005;45(7):792‐801. - PubMed
Teng 2007 {published data only}
-
- Teng YK, Levarht EW, Hashemi M, Bajema IM, Toes RE, Huizinga TW, Laar JM. Immunohistochemical analysis as a means to predict responsiveness to rituximab treatment. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2007;56(12):3909. - PubMed
Teng 2009 {published data only}
-
- Teng YK, Tekstra J, Breedveld FC, Lafeber F, Bijlsma JW, Laar JM. Rituximab fixed retreatment versus on‐demand retreatment in refractory rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of two B cell depleting treatment strategies. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2009;68(6):1075‐7. [PUBMED: 19435725] - PubMed
van den Bemt 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bemt BJF, Vos K, Broeder AA, Blom M, Thurlings RM, Bartelds GM, et al. A single course of rituximab does not abrogate anti‐infliximab antibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2009;68(8):1368‐9. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
August III 2008 {published data only}
-
- A Randomized, Double‐Blind, Placebo Controlled, Multi‐Centre, Exploratory, Pilot, Phase II Trial of 150mg Atacicept Given Subcutaneously in Combination With Rituximab in Subjects With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ongoing study March 2008.
NCT00298272 {published data only}
-
- A Randomized, Double‐Blinded, Placebo Controlled Study to Evaluate the Tolerability and Safety of Rituximab When Given in Combination With Methotrexate and Etanercept (Enbrel) or Methotrexate and Adalimumab (Humira) in Subjects With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ongoing study March 2006.
NCT00422383 {published data only}
-
- A Randomized, Double‐blind Study to Evaluate the Effect of Various Re‐treatment Regimens of MabThera in Combination With Methotrexate on Treatment Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients With an Inadequate Response to Methotrexate. Ongoing study February 2006.
NCT00845832 {published data only}
-
- A Randomized, Active Controlled, Double‐blind, Study to Compare the Safety and Reduction in Disease Activity With the Combination of Rituximab (MabThera®)and Tocilizumab (RoActemra®) Versus Tocilizumab in Patients With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis With an Incomplete Response to Methotrexate. Ongoing study March 2009.
RUMBA {published data only}
-
- A Double‐Blind, Randomized, Multicenter, Phase II Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Two Rituximab Regimens in Subjects With Moderate to Severe Active Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving Stable Doses of Methotrexate. Ongoing study April 2006.
SCORE 2007 {published data only}
-
- A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Multicenter Clinical Study Investigating Efficacy of Rituximab (Mabthera/Rituxan) in the Inhibition of Joint Structural Damage Assessed by Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response to Methotrexate ‐ the RA SCORE Study. Ongoing study November 2007.
Additional references
Arnett 1988
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1988;31(3):315‐24. - PubMed
Bagust 2009
-
- Bagust A, Boland A, Hockenhull J, Fleeman N, Greenhalgh J, Dundar Y, et al. Rituximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Health Technology Assessment 2009;13 Suppl 2:23‐9. [PUBMED: 19804686] - PubMed
Boumas 2009
Bredemeier 2013
-
- Bredemeier M, Oliveira FK, Rocha CM. Low‐ versus high‐dose rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Arthritis Care and Research (Hoboken) 2013;doi::10.1002/acr.22116. [PUBMED: 23983134] - PubMed
Breedveld 2006
-
- Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, Vollenhoven R, et al. The PREMIER study: A multicenter, randomized, double‐blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;54(1):26‐37. - PubMed
Can 2013
-
- Can M1, Alibaz‐Öner F, Yılmaz‐Öner S, Atagündüz P, İnanç N, Direskeneli H. Accelerated infusion rates of rituximab are well tolerated and safe in rheumatology practice: a single‐centre experience. Clinical Rheumatology 2013;32(1):87‐90. [PUBMED: 23053686] - PubMed
Cates 2003
-
- Visual Rx version 2.0. Dr. Christopher Cates EBM website. Available from: URL: http://www.nntonline.net/. Email: visualrx@nntonline.net.
Chatzidionysiou 2013
-
- Chatzidionysiou K, Vollenhoven RF. Rituximab versus anti‐TNF in patients who previously failed one TNF inhibitor in an observational cohort. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 2013;42(3):190‐5. [PUBMED: 23286833] - PubMed
Cohen 2006
-
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti‐tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty‐four weeks. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2006;54(9):2793‐806. - PubMed
Dörner 2003
-
- Dörner T, Burmester GR. The role of B cells in rheumatoid arthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 2003;15(3):246‐52. - PubMed
Edwards 2001
-
- Edwards JC, Cambridge G. Sustained improvement in rheumatoid arthritis following a protocol designed to deplete B lymphocytes. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2001;40:205‐11. - PubMed
Edwards 2004
-
- Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz‐Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. Efficacy of B‐cell‐targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine 2004;350:2572‐81. - PubMed
Felson 1995
-
- Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M, Bombardier C, Furst D, Goldsmith C, et al. American College of Rheumatology. Preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1995;38(6):727‐35. - PubMed
Finckh 2010
-
- Finckh A, Ciurea A, Brulhart L, Moller B, Walker UA, Courvoisier D, et al. on the behalf of the doctors of the Swiss Clinical Quality Management Programme for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Which subgroup of patients with rheumatoid arthritis benefits from switching to rituximab versus alternative anti‐tumour necrosis factor (TNF) agents after previous failure of an anti‐TNF agent?. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69:387‐93. - PMC - PubMed
Fries 1982
-
- Fries JF, Spitz PW, Young DY. The dimensions of health outcomes: the health assessment questionnaire, disability and pain scales. The Journal of Rheumatology 1982;9:789‐93. - PubMed
Fries 1996
-
- Fries JF, Williams CA, Morfeld D, Singh G, Sibley J. Reduction in long‐term disability in patients with rheumatoid arthritis by disease‐modifying antirheumatic drug‐based treatment strategies. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1996;39(4):616‐22. - PubMed
Furst 1994
-
- Furst DE. Considerations on measuring decreased inflammatory synovitis. ILAR Bulletin 1994;2:17‐21.
Genant 1998
-
- Genant HK, Jiang Y, Peterfy C, Redei J, Countryman PJ. Assessment of rheumatoid arthritis using a modified scoring method on digitized and original radiographs. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1998;41(9):1583‐90. [PUBMED: 9751090] - PubMed
Grassi 1998
-
- Grassi W, Angelis R, Lamanna G, Cervini C. The clinical features of rheumatoid arthritis. European Journal of Radiology 1998;27 Suppl 1:S18‐24. - PubMed
Hernandez‐Cruz 2011
-
- Hernandez‐Cruz B, Garcia‐Arias M, Ariza Ariza R, Martin Mola E. Rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of efficacy and safety [Rituximab en artritis reumatoide: una revision sistematica de eficacia y seguridad]. Reumatologia Clinica 2011;7(5):314‐22. - PubMed
Higashida 2005
-
- Higashida J, Wun T, Schmidt S, Naguwa SM, Tuscano JM. Safety and efficacy of rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to disease modifying antirheumatic drugs and anti‐tumor necrosis factor alpha treatment. The Journal of Rheumatology 2005;32:2109‐15. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Isaacs 2013
-
- Isaacs JD, Cohen SB, Emery P, Tak PP, Wang J, Lei G, et al. Effect of baseline rheumatoid factor and anticitrullinated peptide antibody serotype on rituximab clinical response: a meta‐analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2013;72(23):329‐36. [PUBMED: 22689315] - PubMed
Larsen 1973
-
- Larsen A. Radiological grading of rheumatoid arthritis: an interobserver study. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 1973;2:136‐8. - PubMed
Lee 2011
-
- Lee YH, Bae SC, Song GG. The efficacy and safety of rituximab for the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized controlled trials. Rheumatology International 2011;31(11):1493‐9. [PUBMED: 20473756] - PubMed
Lethaby 2013
Lipsky 2000
-
- Lipsky PE, Heijde DM, Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti‐Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. The New England Journal of Medicine 2000;343(22):1594‐602. - PubMed
Lopez‐Olivo 2014
Maneiro 2013
-
- Maneiro RJ, Salgado E, Carmona L, Gomez‐Reino JJ. Rheumatoid factor as predictor of response to abatacept, rituximab and tocilizumab in rheumatoid arthritis: Systematic review and meta‐analysis. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 2013;43(1):9‐17. [PUBMED: 23290690] - PubMed
Maxwell 2009
Mohrbacher 2005
Moots 2012
-
- Moots RJ, Naisbett‐Groet B. The efficacy of biologic agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: a systematic review. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012;51(12):2252‐61. [PUBMED: 22942404] - PubMed
Navarro‐Sarabia 2005
Olsen 2004
-
- Olsen NJ, Stein CM. New drugs for rheumatoid arthritis. The New England Journal of Medicine 2004;350(21):2167‐79. - PubMed
Orme 2012
-
- Orme ME, Macgilchrist KS, Mitchell S, Spurden D, Bird A. Systematic review and network meta‐analysis of combination and monotherapy treatments in disease‐modifying antirheumatic drug‐experienced patients with rheumatoid arthritis: analysis of American College of Rheumatology criteria scores 20, 50, and 70. Biologics 2012;6:429‐64. [PUBMED: 23269860] - PMC - PubMed
Prevoo 1995
-
- Prevoo ML, 't Hof MA, Kuper HH, Leeuwen MA, Putte LB, Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty‐eight‐joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1995;38(1):44‐8. - PubMed
Rigby 2013
-
- Rigby WF, Mease PJ, Olech E, Ashby M, Tole S. Safety of rituximab in combination with other biologic disease‐modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: an open‐label study. The Journal of Rheumatology 2013;40(5):599‐604. - PubMed
Salliot 2009
Schoels 2012
-
- Schoels M, Aletaha D, Smolen JS, Wong JB. Comparative effectiveness and safety of biological treatment options after tumour necrosis factor α inhibitor failure in rheumatoid arthritis: systematic review and indirect pairwise meta‐analysis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2012;71(8):1303‐8. [PUBMED: 22294630] - PubMed
Shetty 2013
-
- Shetty S, Fisher MC, Ahmed AR. Review on the influence of protocol design on clinical outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2013;47(3):311‐23. [PUBMED: 23447479] - PubMed
Singh 2009
Singh 2010
Singh 2010a
-
- Tocilizumab for rheumatoid arthritis. Singh JA, Beg S, Lopez‐Olivo MA. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010;7:CD008331. - PubMed
Singh 2011
Tugwell 1992
-
- Tugwell P, Boers M. OMERACT conference on outcome measures in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials: introduction. The Journal of Rheumatology 1992;20:528‐30. - PubMed
van der Heijde 1999
-
- Heijde DM. How to read radiographs according to the Sharp/van der Heijde method. The Journal of Rheumatology 1999;26:743‐5. - PubMed
Van Gestel 1996
-
- Gestel AM, Prevoo ML, 't Hof MA, Rijswijk MH, Putte LB, Riel PL. Development and validation of the European League Against Rheumatism response criteria for rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with the preliminary American College of Rheumatology and the World Health Organization/International League Against Rheumatism criteria. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1996;39:34‐40. - PubMed
Venkateshan 2009
-
- Venkateshan SP, Sidhu S, Malhotra S, Pandhi P. Efficacy of biologicals in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. A meta‐analysis. Pharmacology 2009;83(1):1‐9. - PubMed
Volkmann 2010
-
- Volkmann ER, Agrawal H, Maranian P, Furst DE. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis: A meta‐analysis and systematic review. Clinical Medicine Insights: Therapeutics 2010;2(2249):749‐60.
Wolfe 1996
-
- Wolfe F. The natural history of rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology 1996;44 Suppl:13‐22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

