MicroRNA-200c contributes to injury from transient focal cerebral ischemia by targeting Reelin
- PMID: 25604249
- PMCID: PMC4346276
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007041
MicroRNA-200c contributes to injury from transient focal cerebral ischemia by targeting Reelin
Abstract
Background and purpose: MicroRNA (miR)-200c increases rapidly in the brain after transient cerebral ischemia but its role in poststroke brain injury is unclear. Reelin, a regulator of neuronal migration and synaptogenesis, is a predicted target of miR-200c. We hypothesized that miR-200c contributes to injury from transient cerebral ischemia by targeting reelin.
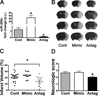
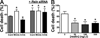
Methods: Brain infarct volume, neurological score and levels of miR-200c, reelin mRNA, and reelin protein were assessed in mice subjected to 1 hour of middle cerebral artery occlusion with or without intracerebroventricular infusion of miR-200c antagomir, mimic, or mismatch control. Direct targeting of reelin by miR-200c was assessed in vitro by dual luciferase assay and immunoblot.
Results: Pretreatment with miR-200c antagomir decreased post-middle cerebral artery occlusion brain levels of miR-200c, resulting in a significant reduction in infarct volume and neurological deficit. Changes in brain levels of miR-200c inversely correlated with reelin protein expression. Direct targeting of the Reln 3' untranslated region by miR-200c was verified with dual luciferase assay. Inhibition of miR-200c resulted in an increase in cell survival subsequent to in vitro oxidative injury. This effect was blocked by knockdown of reelin mRNA, whereas application of reelin protein afforded protection.
Conclusions: These findings suggest that the poststroke increase in miR-200c contributes to brain cell death by inhibiting reelin expression, and that reducing poststroke miR-200c is a potential target to mitigate stroke-induced brain injury.
Keywords: infarction, middle cerebral artery; microRNAs; reperfusion injury; stroke.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
 ), reelin mRNA (
), reelin mRNA ( ) and uncleaved reelin protein (
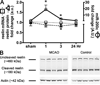
) and uncleaved reelin protein ( ) in mice subjected to 1 hr MCAO. B, Examples of immunoblots for reelin and actin following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) at the 3 hr reperfusion time point. While levels of miR-200c increased by 1 hr of reperfusion (A), levels of uncleaved reelin protein (A, B) decreased by 3 hrs, suggesting translational inhibition. * = p < 0.05 compared to sham control; n = 8 animals/group.
) in mice subjected to 1 hr MCAO. B, Examples of immunoblots for reelin and actin following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) at the 3 hr reperfusion time point. While levels of miR-200c increased by 1 hr of reperfusion (A), levels of uncleaved reelin protein (A, B) decreased by 3 hrs, suggesting translational inhibition. * = p < 0.05 compared to sham control; n = 8 animals/group.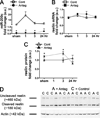

Similar articles
-
Protective action of B1R antagonist against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing miR-200c expression of Microglia-derived microvesicles.Neurol Res. 2017 Jul;39(7):612-620. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2016.1275096. Epub 2017 Apr 11. Neurol Res. 2017. PMID: 28398146
-
MicroRNA-424 protects against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in mice by suppressing oxidative stress.Stroke. 2015 Feb;46(2):513-9. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007482. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Stroke. 2015. PMID: 25523055
-
The Neuroprotective Effect of miR-181a After Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reperfusion and the Associated Mechanism.J Mol Neurosci. 2019 Jun;68(2):261-274. doi: 10.1007/s12031-019-01300-4. Epub 2019 Apr 4. J Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30949956
-
REELIN and schizophrenia: a disease at the interface of the genome and the epigenome.Mol Interv. 2002 Feb;2(1):47-57. doi: 10.1124/mi.2.1.47. Mol Interv. 2002. PMID: 14993361 Review.
-
Go or stop? Divergent roles of Reelin in radial neuronal migration.Neuroscientist. 2010 Aug;16(4):421-34. doi: 10.1177/1073858410367521. Neuroscientist. 2010. PMID: 20817919 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs: protective regulators for neuron growth and development.Neural Regen Res. 2023 Apr;18(4):734-745. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.353481. Neural Regen Res. 2023. PMID: 36204829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced Reelin Expression in the Hippocampus after Traumatic Brain Injury.Biomolecules. 2020 Jun 29;10(7):975. doi: 10.3390/biom10070975. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32610618 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of bioengineered Reelin-loaded PLGA/PEG micelles can accelerate neural tissue regeneration in photothrombotic stroke model of mouse.Bioeng Transl Med. 2021 Oct 29;7(1):e10264. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10264. eCollection 2022 Jan. Bioeng Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 35111956 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional neuronal deletion of microRNA-141/200c cluster, but not microRNA-181a/b-1 cluster, is protective against experimental stroke in male mice.Physiol Rep. 2025 Aug;13(15):e70505. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70505. Physiol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40810631 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs as Emerging Regulators of Neural Injury Responses and Regeneration.Neurosci Bull. 2016 Jun;32(3):253-64. doi: 10.1007/s12264-016-0028-7. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Neurosci Bull. 2016. PMID: 27037691 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Yoon HJ, Jeon D, Kang KM, et al. MicroRNAs induced during ischemic preconditioning. Stroke. 2010;41:1646–1651. - PubMed
-
- Chen CH, Xiao WW, Jiang XB, Wang JW, Mao ZG, Lei N, et al. A novel marine drug, SZ-685C, induces apoptosis of MMQ pituitary tumor cells by downregulating miR-200c. Curr Med Chem. 2013;20:2145–2154. - PubMed
-
- D’Arcangelo G, Miao GG, Chen SC, Soares HD, Morgan JI, Curran T. A protein related to extracellular matrix proteins deleted in the mouse mutant reeler. Nature. 1995;374:719–723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

