Randomized multicenter phase III study of a modified docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil regimen compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced or locally recurrent gastric cancer
- PMID: 25604851
- PMCID: PMC4688303
- DOI: 10.1007/s10120-015-0457-4
Randomized multicenter phase III study of a modified docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil regimen compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced or locally recurrent gastric cancer
Abstract
Background: The V325 study showed that docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil (DCF) prolonged overall survival (OS) of patients with advanced gastric cancer, but with a high incidence of dose-limiting toxicities. We investigated the efficacy and safety of a modified DCF (mDCF) regimen for Chinese patients with advanced gastric cancer.
Methods: Untreated advanced gastric cancer patients randomly received docetaxel and cisplatin at 60 mg/m(2) (day 1) followed by fluorouracil at 600 mg/m(2)/day (days 1-5; mDCF regimen) or cisplatin at 75 mg/m(2) (day 1) followed by fluorouracil at 600 mg/m(2)/day (days 1-5; CF) every 3 weeks. The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS). The secondary end points were OS, overall response rate (ORR), time-to-treatment failure (TTF), and safety.
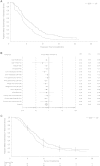
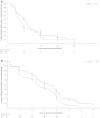
Results: In total, 243 patients were randomized to treatment (mDCF regimen 121; CF 122). Compared with CF, the mDCF regimen significantly improved PFS and OS: the median PFS was 7.2 and 4.9 months, respectively [hazard ratio (HR) 0.58, log-rank P = 0.0008], and the median OS was 10.2 and 8.5 months, respectively (HR = 0.71, P = 0.0319). Additionally, the mDCF regimen improved the parameters used as secondary objectives: the ORR was 48.7% with the mDCF regimen versus 33.9% with CF (P = 0.0244); the median TTF was 3.4 months with the mDCF regimen and 2.4 months with CF (HR = 0.67, P = 0.0027). Grade 3 and grade 4 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 77.3 % of patients who received the mDCF regimen versus 46.1% of patients who received CF (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: The mDCF regimen, compared with CF, significantly prolonged PFS and OS and enhanced ORR of Chinese patients with advanced gastric cancer. The mDCF regimen achieved efficacy comparable to that of DCF but with fewer toxicities, which is appropriate for the Chinese population.
Keywords: Advanced gastric cancer; Modified docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil regimen; Overall survival; Progression-free survival; Safety.
Figures

References
-
- Van Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, et al. Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: a report of the V325 Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4991–4997. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.8429. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

