Anti-inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids on TNBS-induced Colitis of Rats
- PMID: 25605996
- PMCID: PMC4297761
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2015.19.1.43
Anti-inflammatory Effects of Flavonoids on TNBS-induced Colitis of Rats
Abstract
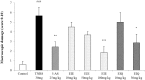
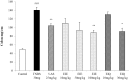
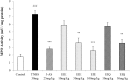
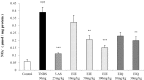
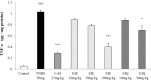
It has been shown that the extracts including eupatilin and quercetin-3-β-D-glucuronopyranoside had mucoprotective effects on the esophagus and stomach through their antioxidant activities. This study was designed to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of these flavonoid compounds in an animal model of inflammatory bowel disease induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. Experimental colitis was induced by intracolonic administration of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid. Extracts including eupatilin or quercetin-3-β-D-glucuronopyranoside were orally administered to animals 48, 24, and 1 h prior to the induction of colitis and then again 24 h later. The animals were sacrificed 48 h after by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid treatment and the macroscopic appearance of the colonic lesions was scored in a blinded manner on a scale of 1 to 10. The inflammatory response to colitis induction was assessed by measuring myeloperoxidase activity, nitric oxide production, tumor necrosis factor-α expression, total glutathione levels, and malondialdehyde concentrations in the colon. The results indicated that extracts including eupatilin and extracts including quercetin-3-β-D-glucuronopyranoside dose-dependently improved the morphology of the lesions induced by 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid and reduced the ulcer index accordingly. In addition, rats receiving extracts including eupatilin and extracts including quercetin-3-β-D-glucuronopyranoside showed significantly decreased levels of mucosal myeloperoxidase activity, nitric oxide production, tumor necrosis factor-α expression, and malondialdehyde levels, and increased total glutathione levels. Extracts including eupatilin and extracts including quercetin-3-β-D-glucuronopyranoside ameliorated the inflammatory response and colonic injury in acute colitis by decreasing oxidative stress and neutrophil activation. Extracts including eupatilin and extracts including quercetin-3-β-D-glucuronopyranoside may inhibit acute colitis.
Keywords: Colitis; Flavonoids; Inflammation; Quercetin; Reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- da Silva MS, Sánchez-Fidalgo S, Talero E, Cárdeno A, da Silva MA, Villegas W, Souza Brito AR, de La Lastra CA. Anti-inflammatory intestinal activity of Abarema cochliacarpos (Gomes) Barneby & Grimes in TNBS colitis model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010;128:467–475. - PubMed
-
- Yao J, Wang JY, Liu L, Li YX, Xun AY, Zeng WS, Jia CH, Wei XX, Feng JL, Zhao L, Wang LS. Anti-oxidant effects of resveratrol on mice with DSS-induced ulcerative colitis. Arch Med Res. 2010;41:288–294. - PubMed
-
- Elson CO, Sartor RB, Tennyson GS, Riddell RH. Experimental models of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1995;109:1344–1367. - PubMed
-
- van Assche G, Rutgeerts P. Antiadhesion molecule therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2002;8:291–300. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

