PSMA6 (rs2277460, rs1048990), PSMC6 (rs2295826, rs2295827) and PSMA3 (rs2348071) genetic diversity in Latvians, Lithuanians and Taiwanese
- PMID: 25606411
- PMCID: PMC4287955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mgene.2014.03.002
PSMA6 (rs2277460, rs1048990), PSMC6 (rs2295826, rs2295827) and PSMA3 (rs2348071) genetic diversity in Latvians, Lithuanians and Taiwanese
Abstract
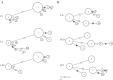
PSMA6 (rs2277460, rs1048990), PSMC6 (rs2295826, rs2295827) and PSMA3 (rs2348071) genetic diversity was investigated in 1438 unrelated subjects from Latvia, Lithuania and Taiwan. In general, polymorphism of each individual locus showed tendencies similar to determined previously in HapMap populations. Main differences concern Taiwanese and include presence of rs2277460 rare allele A not found before in Asians and absence of rs2295827 rare alleles homozygotes TT observed in all other human populations. Observed patterns of SNPs and haplotype diversity were compatible with expectation of neutral model of evolution. Linkage disequilibrium between the rs2295826 and rs2295827 was detected to be complete in Latvians and Lithuanians (D´ = 1; r(2) = 1) and slightly disrupted in Taiwanese (D´ = 0.978; r(2) = 0.901). Population differentiation (FST statistics) was estimated from pairwise population comparisons of loci variability, five locus haplotypes and PSMA6 and PSMC6 two locus haplotypes. Latvians were significantly different from all Asians at each of 5 SNPs and from Lithuanians at the rs1048990 and PSMC6 loci. Lithuanian and Asian populations exhibited similarities at the PSMC6 loci and were different at the PSMA6 and PSMA3 SNPs. Considering five locus haplotypes all European populations were significantly different from Asian; Lithuanian population was different from both Latvian and CEU. Allele specific patterns of transcription factor binding sites and splicing signals were predicted in silico and addressed to eventual functionality of nucleotide substitutions and their potential to be involved in human genome evolution and geographical adaptation. Current study represents a novel step toward a systematic analysis of the proteasomal gene genetic diversity in human populations.
Keywords: Genetic diversity; HWE, Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium; HapMap HCB, Han Chinese; HapMap JPT, Japanese; HapMap-CEU, NorthWestern Europeans; Human population; LD, linkage disequilibrium; LT, Lithuanian population; LV, Latvian population; PSMA3; PSMA6; PSMC6; Proteasome; SNP; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; TF, transcription factor; TFBS, transcription factor binding site; TW, Taiwanese population; UPS, ubiquitin–proteasome system.
Figures


References
-
- Alsmadi O., Muiya P., Khalak H. Haplotypes encompassing the KIAA0391 and PSMA6 gene cluster confer a genetic link for myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2009;73:475–483. - PubMed
-
- Arbouzova N.I., Bach E.A., Zeidler M.P. Ken & Barbie selectively regulates the expression of a subset of Jak/STAT pathway target genes. Curr. Biol. 2006;16:80–88. - PubMed
-
- Bachmann H.S., Novotny J., Sixt S. The G-allele of the PSMA6-8G>C polymorphism is associated with poor outcome in multiple myeloma independently of circulating proteasome serum levels. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010;85:108–113. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee I., Gupta V., Ahmed T. Inflammatory system gene polymorphism and the risk of stroke: a case–control study in an Indian population. Brain Res. Bull. 2008;75:158–165. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee I., Pandey U., Hasan O.M. Association between inflammatory gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in an Indian population. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis. 2009;27:88–94. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

