Keratin 13 mutations associated with oral white sponge nevus in two Chinese families
- PMID: 25606422
- PMCID: PMC4287858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mgene.2014.04.008
Keratin 13 mutations associated with oral white sponge nevus in two Chinese families
Abstract
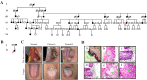
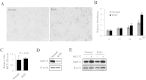
White sponge nevus (WSN) is an autosomal dominant hereditary disease. Keratin 4 (KRT4) and Keratin 13 (KRT13) gene mutations were involved in the WSN. We recruited two WSN Chinese families, and oral lesion biopsy with hematoxylin and eosin staining showed that patients had significant pathological characteristics. The mutations of KRT4 and KRT13 gene were detected by PCR and direct sequencing. The multiple alignments of KRT13 from 23 diverse species homology analyses were performed by the ClustalW program. The KRT13 expression was measured by Real-Time RT-PCR and Western blot analysis. Sequencing analysis revealed two mutations of KRT13 gene: one mutation was 332T>C and amino acid change was Leu111Pro. Another mutation was 340C>T and amino acid change was Arg114Cys. The sequence of KRT13 was highly conserved. Real-Time RT-PCR and Western blot analysis results show that KRT13 expression level is lower in patient but keep almost no change in mRNA level. When cells were treated with MG132, KRT13 protein level was increased and kept almost the same in normal and patient cells. We identified two heritable mutations in the KRT13 gene, which were associated with the development of WSN. The abnormal degradation of KRT13 protein of WSN may probably associate with the abnormal ubiquitination process.
Keywords: Gene mutation; Keratin 13 (KRT13); Oral disease; Ubiquitination; White sponge nevus (WSN).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression profiling of white sponge nevus by RNA sequencing revealed pathological pathways.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015 Jun 11;10:72. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0285-y. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015. PMID: 26062705 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical features and molecular genetic analysis in a Turkish family with oral white sponge nevus.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2018 Mar 1;23(2):e144-e150. doi: 10.4317/medoral.21437. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2018. PMID: 29476668 Free PMC article.
-
Keratin 13 deficiency causes white sponge nevus in mice.Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 1;468(1-2):146-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.07.016. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32758484 Free PMC article.
-
Current approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of white sponge nevus.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015 May 29;17:e9. doi: 10.1017/erm.2015.7. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26021387 Review.
-
Human keratin diseases: hereditary fragility of specific epithelial tissues.Exp Dermatol. 1996 Dec;5(6):297-307. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1996.tb00133.x. Exp Dermatol. 1996. PMID: 9028791 Review.
Cited by
-
Keratin 13 Is Enriched in Prostate Tubule-Initiating Cells and May Identify Primary Prostate Tumors that Metastasize to the Bone.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 6;11(10):e0163232. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163232. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27711225 Free PMC article.
-
White sponge nevus: Report of three cases in a single family.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2016 May-Aug;20(2):300-3. doi: 10.4103/0973-029X.185915. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27601826 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Potentially Pathogenic Variants Associated with Recurrence in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (MRONJ) Patients Using Whole-Exome Sequencing.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 12;11(8):2145. doi: 10.3390/jcm11082145. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35456240 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiling of white sponge nevus by RNA sequencing revealed pathological pathways.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015 Jun 11;10:72. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0285-y. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015. PMID: 26062705 Free PMC article.
-
White Sponge Nevus Caused by Keratin 4 Gene Mutation: A Case Report.Genes (Basel). 2022 Nov 22;13(12):2184. doi: 10.3390/genes13122184. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alinovi A., Benoldi D., Pezzarossa E. White sponge nevus: successful treatment with penicillin. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1982;63:83–85. - PubMed
-
- Becker L., Lutz C., Erbard H., Bröcker E., Hamm H. White sponge naevus successfully treated with tetracycline mouth rinse. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1997;77:413. - PubMed
-
- Cannon A. White sponge nevus of the mucosa (naevus spongiosus albus mucosae) Arc. Dermatol. 1935;31:365.
-
- Chao S., Tsai Y., Yang M., Lee J. A novel mutation in the keratin 4 gene causing white sponge naevus. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003;148:1125–1128. - PubMed
-
- Dufrasne L., Magremanne M., Parent D., Evrard L. Current therapeutic approach of the white sponge naevus of the oral cavity. Bull. Group. Int. Rech. Sci. Stomatol. Odontol. 2011;50:1–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

