The healing effect of scrophularia striata on experimental burn wounds infected to pseudomonas aeruginosa in rat
- PMID: 25606472
- PMCID: PMC4298860
The healing effect of scrophularia striata on experimental burn wounds infected to pseudomonas aeruginosa in rat
Abstract
Background: The cause of death in burn patients after 48 hours of hospitalization has been reported to be bacterial infections. Recently, due to the compounds accelerating the healing process and the intense reduction of treatment side effects, medicinal plants are used to cure burn wound infections. This study aims to investigate the medicinal effect of the ethanolic extract of Scrophularia striata on burn wound infection in in-vivo and in-vitro in comparison with silver sulfadiazine (SSD).
Methods: One hundred and fifty male Sprague Dawley rats were divided into 3 equal groups. A hot plate of 1×1cm was used to create second degree burn wounds. The ethanolic extract of S. striata was provided through percolation method. Group 1 was treated with SSD, group 2 with S. striata, and group 3 was considered as control group. All animals were infected to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. On days 3, 7, 10, 14, and 21 after burn wound injury, the animals were euthanized and were evaluated histologically. The MIC and MBC were determined using the micro dilution method.
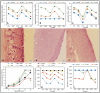
Results: The rate of wound healing was significantly greater in S. striata group in comparison to SSD and control groups.
Conclusion: S. striata contains was shown to have anti-bacterial and wound healing effects while this effect was significantly more than SSD denoting to its use when needed for burn wounds infected to P. aeruginosa.
Keywords: Healing; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Scrophularia striata; Silver sulfadiazine; Wound.
Figures

References
-
- Mohammadi AA, Amini M, Mehrabani D, Kiani Z, Seddigh A. A survey on 30 months electrical burns in Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Burn Hospital. Burns. 2008;34:111–3. - PubMed
-
- Pasalar M, Mohammadi AA, Rajaeefard AR, Neghab M, Tolidie HR, Mehrabani D. Epidemiology of burns during pregnancy in southern Iran: Effect on maternal and fetal outcomes. World Appl Sci J. 2013;28:153–8.
-
- Rezaei E, Safari H, Motamedolshariati SM, Afzal Aghaei M. Analysis of mortality in a burn center. J Mashad Univ Med Sci. 2010;52:239–43.
-
- Cakir B, Yegen BC. Systemic responses to burn injury. Turkish J Med Sci. 2004;34:215–26.
-
- Karimi Estahbanati H, Pourkashani P, Ghanaatpisheh F. Frequency of Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotypes in burn wound infections and their resistance to antibiotics. Burns. 2002;28:340–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
