The Healing Effects of Aquatic Activities and Allogenic Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) on Injuries of Achilles Tendon in Experimental Rat
- PMID: 25606479
- PMCID: PMC4298867
The Healing Effects of Aquatic Activities and Allogenic Injection of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) on Injuries of Achilles Tendon in Experimental Rat
Abstract
Background: Clinical tendon injuries represent serious and unresolved issues of the case on how the injured tendons could be improved based on natural structure and mechanical strength. The aim of this studies the effect of aquatic activities and alogenic platelet rich plasma (PRP) injection in healing Achilles tendons of rats.
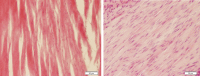
Methods: Forty rats were randomly divided into 5 equal groups. Seventy two hours after a crush lesion on Achilles tendon, group 1 underwent aquatic activity for 8 weeks (five sessions per week), group 2 received intra-articular PRP (1 ml), group 3 had aquatic activity together with injection PRP injection after an experimental tendon injury, group 4 did not receive any treatment after tendon injury and the control group with no tendon injuries. of 32 rats. After 8 weeks, the animals were sacrificed and the tendons were transferred in 10% formalin for histological evaluation.
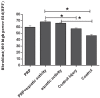
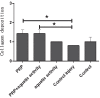
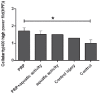
Results: There was a significant increase in number of fibroblast and cellular density, and collagen deposition in group 3 comparing to other groups denoting to an effective healing in injured tendons. However, there was no significant difference among the studied groups based on their tendons diameter.
Conclusion: Based on our findings on the number of fibroblast, cellular density, collagen deposition, and tendon diameter, it was shown that aquatic activity together with PRP injection was the therapeutic measure of choice enhance healing in tendon injuries that can open a window in treatment of damages to tendons.
Keywords: Aquatic activities; Healing; Platelet Rich Plasma; Rat; Tendon.
Figures
References
-
- Nikahval B, Dehghani SN, Bagheri MH, Pakbaz S, Mansourian M, Tanideh N, Mehrabani D, Alirezaei M. Correlations between radiographic, magnetic resonance imaging and histopathologic fi ndings in experimentally ruptured cranial cruciate in experimentally ruptured cranial cruciate ligament joints in rabbits. Vet Arhiv. 2013;83:537–50.
-
- Tanideh N, Bagheri MH, Dehghani Nazhvani S, Nikahval B, Mojtahed Jaberi F, Mehrabani D. MRI and CT evaluations of an invented bioglue in experimentally induced articular cartilage defects in rabbits. Comp Clin Pathol. 2014;23:1545–50.
-
- Bagheri MH, Dehghani Nzhvani S, Nikahval B, Pakbaz S, Tanideh N, Mehrabani D. Articular cartilage changes in experimental osteoarthriris in rabbits: MRI and morphological findings. Comp Clin Pathol. 2011;20:25–31.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
