Beta-catenin is elevated in human benign prostatic hyperplasia specimens compared to histologically normal prostate tissue
- PMID: 25606577
- PMCID: PMC4297327
Beta-catenin is elevated in human benign prostatic hyperplasia specimens compared to histologically normal prostate tissue
Abstract
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is linked to lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) such as incomplete bladder emptying, urinary frequency and urgency. Mechanisms responsible for BPH are not fully known. Here, we tested whether beta-catenin (CTNNB1) immunostaining intensity and distribution differ in human glandular BPH tissue specimens compared to normal prostate tissue. Multiplex immunostaining of CTNNB1, its putative transcriptional target gene lymphoid enhancer binding factor 1 (LEF1), and the epithelial marker E-cadherin were examined in clinical human prostate specimens with or without histological BPH (pure epithelial or mixed stromal-epithelial nodules). BPH specimens were obtained from 24 men who experienced LUTS and underwent transurethral resection of the prostate surgery. Control specimens were tumor-adjacent histologically normal prostate tissue from 48 patients who underwent radical prostatectomy. The resulting multispectral images were unmixed and optical densities recorded to quantify staining abundance, cellular (membranous, cytoplasmic, and nuclear) and tissue localization (stromal versus epithelial), and determination of percentage of CTNNB1-positive cells. The following CTNNB1 indices were significantly higher in BPH compared to normal prostate tissue: overall staining intensity, staining intensity in prostate stromal cell membranes, cytoplasm and nuclei, and prostate epithelial cell nuclei. The following LEF1 indices were significantly lower in BPH compared to tumor-adjacent normal prostate tissue: stromal LEF1 staining intensity, percentage of LEF1-positive stromal cells, and intensity of LEF1 staining in stromal cell membranes, cytoplasm, and nuclei. The percentage of stromal cells with CTNNB1(+)/LEF1(-) nuclei was higher and percentage of stromal cells with CTNNB1(-)/LEF1(+) nuclei was lower in BPH compared to tumor-adjacent normal prostate tissues. These results support the hypothesis that CTNNB1 expression increases in specific BPH tissue compartments. Further, since nuclear LEF1 staining does not coincide with cytoplasmic or nuclear CTNNB1 staining, it does not appear to be a reliable index of CTNNB1 activity in adult human prostate.
Keywords: LEF1; Prostate; beta-catenin; cellular localization; multispectral; stromal-epithelial; tissue microarray.
Figures
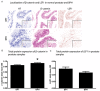
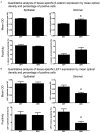
References
-
- Mishra VC, Allen DJ, Nicolaou C, Sharif H, Hudd C, Karim OM, Motiwala HG, Laniado ME. Does intraprostatic inflammation have a role in the pathogenesis and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia? BJU Int. 2007;100:327–331. - PubMed
-
- Di Silverio F, Gentile V, De Matteis A, Mariotti G, Giuseppe V, Luigi PA, Sciarra A. Distribution of inflammation, pre-malignant lesions, incidental carcinoma in histologically confirmed benign prostatic hyperplasia: a retrospective analysis. Eur Urol. 2003;43:164–175. - PubMed
-
- Roehrborn CG, Kaplan SA, Noble WD, Lucia MS, Slawin KM, McVary KT. The impact of acute or chronic inflammation in basaeline biopsy on the risk of clinical progression of BPE: results from the MTOPS study. 2005 May 21-25; San Antonio, TX.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
