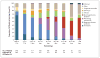
Causes and timing of death in extremely premature infants from 2000 through 2011
- PMID: 25607427
- PMCID: PMC4349362
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1403489
Causes and timing of death in extremely premature infants from 2000 through 2011
Abstract
Background: Understanding the causes and timing of death in extremely premature infants may guide research efforts and inform the counseling of families.
Methods: We analyzed prospectively collected data on 6075 deaths among 22,248 live births, with gestational ages of 22 0/7 to 28 6/7 weeks, among infants born in study hospitals within the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. We compared overall and cause-specific in-hospital mortality across three periods from 2000 through 2011, with adjustment for baseline differences.
Results: The number of deaths per 1000 live births was 275 (95% confidence interval [CI], 264 to 285) from 2000 through 2003 and 285 (95% CI, 275 to 295) from 2004 through 2007; the number decreased to 258 (95% CI, 248 to 268) in the 2008-2011 period (P=0.003 for the comparison across three periods). There were fewer pulmonary-related deaths attributed to the respiratory distress syndrome and bronchopulmonary dysplasia in 2008-2011 than in 2000-2003 and 2004-2007 (68 [95% CI, 63 to 74] vs. 83 [95% CI, 77 to 90] and 84 [95% CI, 78 to 90] per 1000 live births, respectively; P=0.002). Similarly, in 2008-2011, as compared with 2000-2003, there were decreases in deaths attributed to immaturity (P=0.05) and deaths complicated by infection (P=0.04) or central nervous system injury (P<0.001); however, there were increases in deaths attributed to necrotizing enterocolitis (30 [95% CI, 27 to 34] vs. 23 [95% CI, 20 to 27], P=0.03). Overall, 40.4% of deaths occurred within 12 hours after birth, and 17.3% occurred after 28 days.
Conclusions: We found that from 2000 through 2011, overall mortality declined among extremely premature infants. Deaths related to pulmonary causes, immaturity, infection, and central nervous system injury decreased, while necrotizing enterocolitis-related deaths increased. (Funded by the National Institutes of Health.).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Mathews TJ, MacDorman MF. Infant mortality statistics from the 2009 period linked birth/infant death data set. Hyattsville, MD: National Centers for Health Statistics; 2013. ( http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_08.pdf) - PubMed
-
- Lemons JA, Bauer CR, Oh W, et al. Very low birth weight outcomes of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network, January 1995 through December 1996. Pediatrics. 2001;107(1):E1. - PubMed
-
- Gould JB, Benitz WE, Liu H. Mortality and time to death in very low birth weight infants: California, 1987 and 1993. Pediatrics. 2000;105(3):E37. - PubMed
-
- Mohamed MA, Nada A, Aly H. Day-by-day postnatal survival in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 2010;126(2):e360–e366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U10 HD27851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD068263/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68284/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000455/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68278/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- KL2TR000455/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD068270/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD068244/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD087229/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068244/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068263/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68263/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068270/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD068284/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068284/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD068278/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21415/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68270/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD68244/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD068278/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27881/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical