Identification of structural DNA variations in human cell cultures after long-term passage
- PMID: 25607645
- PMCID: PMC4353222
- DOI: 10.4161/15384101.2014.974427
Identification of structural DNA variations in human cell cultures after long-term passage
Abstract
Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) analysis was adapted for genomic identification of cell cultures and evaluation of DNA stability in cells of different origin at different culture passages. DNA stability was observed in cultures after no more than 5 passages. Adipose-derived stromal cells demonstrated increased DNA instability. RAPD fragments from different cell lines after different number of passages were cloned and sequenced. The chromosomal localization of these fragments was identified and single-nucleotide variations in RAPD fragments isolated from cell lines after 8-12 passages were revealed. Some of them had permanent localization, while most variations demonstrated random distribution and can be considered as de novo mutations.
Keywords: Cell cultures; DNA stability in cells; Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD); different number of passages; mutations.
Figures
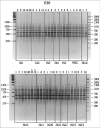
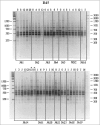
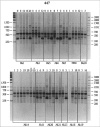
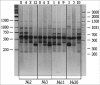
References
-
- Tarte K, Gaillard J, Lataillade JJ, Fouillard L, Becker M, Mossafa H, Tchirkov A, Rouard H, Henry C, Splingard M, et al. Clinical-grade production of human mesenchymal stromal cells: occurrence of aneuploidy without transformation. Blood 2010; 115(8):1549-53; PMID:; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1182/blood-2009-05-219907 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sensebé L, Bourin P, Tarte K. Good manufacturing practices production of mesenchymal stemstromal cells. Hum Gene Ther 2011; 22(1):19-26; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1089/hum.2010.197 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ueyama H, Horibe T, Hinotsu S, Tanaka T, Inoue T, Urushihara H, Kitagawa A, Kawakami K. Chromosomal variability of human mesenchymal stem cells cultured under hypoxic conditions. J Cell Mol Med 2012; 16(1):72-82; PMID:; http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01303.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pradel W, Mai R, Gedrange T, Lauer GJ. Cell passage and composition of culture medium effects proliferation and differentiation of human osteoblast-like cells from facial bone. Physiol Pharmacol 2008; 59(5):47-58; PMID: - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
