Influence of levosimendan postconditioning on apoptosis of rat lung cells in a model of ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 25608001
- PMCID: PMC4301642
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114963
Influence of levosimendan postconditioning on apoptosis of rat lung cells in a model of ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
Objective: To ascertain if levosimendan postconditioning can alleviate lung ischemia-reperfusion injury (LIRI) in rats.
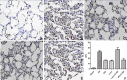
Method: One hundred rats were divided into five groups: Sham (sham), ischemia-reperfusion group (I/R group), ischemic postconditioning (IPO group), levosimendan postconditioning (Levo group) and combination postconditioning group of levosimendan and 5-Hydroxydecanoic acid (Levo+5-HD group). The apoptotic index (AI) of lung tissue cells was determined using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Expression of active cysteine aspartate specific protease-3 ( active caspase-3), Bcl-2 and Bax in lung tissue was determined by immunohistochemical staining. The morphopathology of lung tissue was observed using light and electron microscopy.
Results: AI values and expression of active caspase-3, Bcl-2 and Bax of lung tissue in I/R and Levo+5-HD groups were significantly higher than those in the sham group ( P<0.05). AI values and expression of active caspase-3 and Bax were significantly lower, whereas that of Bcl-2 was higher significantly in the Levo group, compared with I/R and Levo+5-HD groups (P<0.05). Significant differences were not observed in comparisons between I/R and Levo+5-HD groups as well as IPO and Levo groups.
Conclusion: LIRI can be alleviated by levosimendan, which simulates an IPO protective function. A postulated lung-protective mechanism of action could involve opening of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels, relieving Ca2+ overload, upregulation of expression of Bcl-2, and downregulation of expression of active caspase-3 and Bax.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



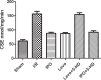
Similar articles
-
[Ischemic postconditioning attenuates pneumocyte apoptosis after lung ischemia/reperfusion injury via inactivation of p38 MAPK].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014 May;30(3):251-6. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25244794 Chinese.
-
Levosimendan protection against kidney ischemia/reperfusion injuries in anesthetized pigs.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Aug;342(2):376-88. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.193961. Epub 2012 May 7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22566668
-
[Effects of ischemic postconditioning on pneumocyte apoptosis after lung ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Jan;30(1):60-3. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24741980 Chinese.
-
[Protective effects and mechanism of SP600125 on lung ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012 May;28(3):255-8. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22860429 Chinese.
-
The protective effects of levosimendan on ischemia/reperfusion injury and apoptosis.Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2011 Jan;6(1):20-6. doi: 10.2174/157489011794578482. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21208156 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of expressions of Bcl-XL, b-FGF, Bmp-2, Caspase-3, PDGFR-α, Smad1 and TGF-β1 genes in a rat model of lung ischemia/reperfusion.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016 Feb;19(2):209-14. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27081467 Free PMC article.
-
TT-1, an analog of melittin, triggers apoptosis in human thyroid cancer TT cells via regulating caspase, Bcl-2 and Bax.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jan;15(1):1271-1278. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.7366. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29387245 Free PMC article.
-
Lung injury after asphyxia and hemorrhagic shock in newborn piglets: Analysis of structural and inflammatory changes.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 5;14(7):e0219211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219211. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31276543 Free PMC article.
-
Ex Vivo Lung Perfusion with K(ATP) Channel Modulators Antagonize Ischemia Reperfusion Injury.Cells. 2021 Sep 3;10(9):2296. doi: 10.3390/cells10092296. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34571948 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of post-reperfusion levosimendan in an experimental intestinal ischemia-reperfusion model.J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2022 Oct 27;2(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s44158-022-00074-3. J Anesth Analg Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 37386547 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

