Reliability and application variability of a commercially available infrared videonystagmography unit
- PMID: 25608282
- PMCID: PMC4725705
- DOI: 10.3928/01913913-20150114-04
Reliability and application variability of a commercially available infrared videonystagmography unit
Erratum in
-
Erratum for "Reliability and Application Variability of a Commercially Available Infrared Videonystagmography Unit".J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2015 May-Jun;52(3):167. doi: 10.3928/01913913-20150427-11. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2015. PMID: 26053208 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary eye movement. The causes for nystagmus may be congenital, idiopathic, or acquired. Considerable debate exists on the therapeutic potential of various surgical techniques. Currently, there are neither standardized protocols nor devices to record quantitative data on patients with clinical nystagmus undergoing various procedures at multiple centers to facilitate randomized prospective clinical trials.
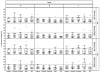
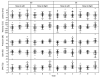
Methods: The authors evaluated the reliability and variability of a commercially available infrared videonystagmography unit by recording eye movement waveforms elicited from normal volunteers (n = 117, 13 patients, 9 trials) by different examiners (A, B, and C). Five movement characteristics were examined, including saccadic latency, velocity and precision, and pursuit gain and velocity.
Results: The overall test/retest variability was low, where the median coefficient of variation of the three testers for all five eye movement categories was less than 15%, and less than 10% of the coefficients of variation calculated were more than 20%. However, there was a significant difference in interobserver variability for all outcomes, except saccade latency.
Conclusions: The between-tester analysis was found to have greater variability than the test/retest reliability analysis. Future studies at multiple sites using videonystagmography measurements should aim to have each patient repeatedly tested by the same tester. In anticipation of multicenter, randomized, prospective clinical trials of surgical procedures for nystagmus, standardized protocols for nystagmographic data collection and analysis must be validated both within and among participating centers.
Copyright 2015, SLACK Incorporated.
Figures
References
-
- Lee JP. Surgical management of nystagmus. Eye. 1988;2(Pt 1):44–47. - PubMed
-
- Abel LA. Infantile nystagmus: current concepts in diagnosis and management. Clinical & experimental optometry : journal of the Australian Optometrical Association. 2006 Mar;89(2):57–65. - PubMed
-
- Collewijn H, van der Mark F, Jansen TC. Precise recording of human eye movements. Vision research. 1975 Mar;15(3):447–450. - PubMed
-
- Robinson DA. A Method of Measuring Eye Movement Using a Scleral Search Coil in a Magnetic Field. IEEE transactions on bio-medical engineering. 1963 Oct;10:137–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

