Prescribing efficiency of proton pump inhibitors in China: influence and future directions
- PMID: 25609265
- PMCID: PMC4308879
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-014-0638-6
Prescribing efficiency of proton pump inhibitors in China: influence and future directions
Abstract
Background: Pharmaceutical expenditure is currently rising by 16% per annum in China, greater in recent years. Initiatives to moderate growth include drug pricing regulations, essential medicine lists and encouraging generic prescribing. These are principally concentrated in hospitals, which currently account for over 80% of total pharmaceutical expenditure. However, no monitoring of prescribing and perverse incentives encouraging physicians and hospitals to profit from drug procurement encourages irrational prescribing. This includes greater utilisation of originators versus generics as well as injectables when cheaper oral equivalents are available. The objective of the paper is to assess changes in proton pump inhibitor (PPI) utilisation and expenditure in China as more generics become available including injectables.
Methods: Observational retrospective study of PPI utilisation and procured expenditure between 2004 and 2013 in the largest teaching hospital in Chongqing District as representative of China.
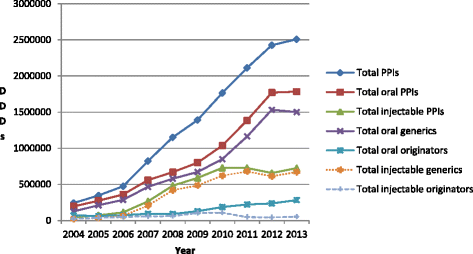
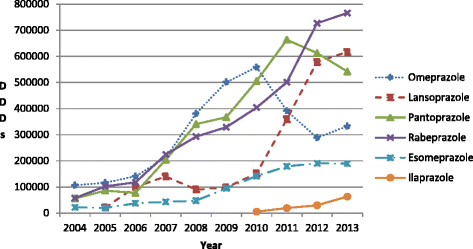
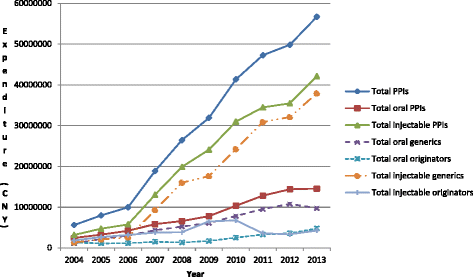
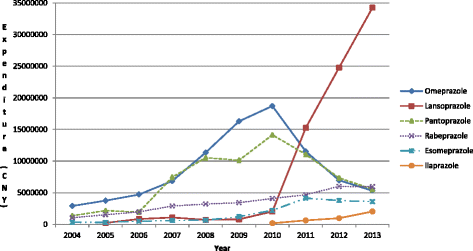
Results: Appreciable increase in PPI utilisation during the study period rising 10.4 fold, with utilisation of generics rising faster than originators. Oral generics reached 84% of total oral preparations in 2013 (defined daily dose basis), with generic injectables 93% of total injectables by 2013. Injectables accounted for 42% of total PPI utilisations in 2008 and 2009 before falling to below 30%. Procured prices for oral preparations reduced over time (-34%). Generic oral omeprazole in 2010 was 87% below 2004 originator prices, mirroring reductions seen in Western Europe. Injectable prices also decreased over time (-19%). However, injectables typically 4.3 to 6.8 fold more expensive than equivalent orals - highest for injectable lansoprazole at 13.4 to 18.0 fold. High utilisation of more expensive oral PPIs as well as injectables meant that PPI expenditure increased 10.1 fold during the study period. Lower use of injectables, and only oral generic omeprazole, would result in accumulated savings of CNY249.65 million, reducing total accumulated expenditure by 84%.
Conclusions: Encouraging to see high utilisation of generic PPIs and low prices for oral generics. However, considerable opportunities to enhance prescribing efficiency through greater use of oral generic omeprazole.
Figures
References
-
- OECD. OECD, Health at a Glance 2011: OECD Indicators. Available at URL: http://www.oecd.org/els/health-systems/49105858.pdf
-
- Vogler S, Zimmermann N, Habl C. Understanding the components of pharmaceutical expenditure - overview of pharmaceutical policies influencing expenditure across European countries. GaBi J. 2013;2(3):178–187. doi: 10.5639/gabij.2013.0204.051. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

