HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity and phytocomponent investigation of Basella alba leaf extract as a treatment for hypercholesterolemia
- PMID: 25609924
- PMCID: PMC4298350
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S75056
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity and phytocomponent investigation of Basella alba leaf extract as a treatment for hypercholesterolemia
Abstract
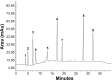
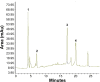
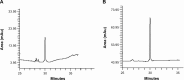
The enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase is the key enzyme of the mevalonate pathway that produces cholesterol. Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase reduces cholesterol biosynthesis in the liver. Synthetic drugs, statins, are commonly used for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Due to the side effects of statins, natural HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of plant origin are needed. In this study, 25 medicinal plant methanol extracts were screened for anti-HMG-CoA reductase activity. Basella alba leaf extract showed the highest inhibitory effect at about 74%. Thus, B. alba was examined in order to investigate its phytochemical components. Gas chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry and reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography analysis revealed the presence of phenol 2,6-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl), 1-heptatriacotanol, oleic acid, eicosyl ester, naringin, apigenin, luteolin, ascorbic acid, and α-tocopherol, which have been reported to possess antihypercholesterolemic effects. Further investigation of in vivo models should be performed in order to confirm its potential as an alternative treatment for hypercholesterolemia and related cardiovascular diseases.
Keywords: Basella alba; GC-MS/MS; HMG-CoA reductase; RP-HPLC; hypercholesterolemia; phytochemical.
Figures
References
-
- Gholamhoseinian A, Sharifi-Far F, Shahouzehi B. Inhibitory activity of some plant methanol extracts on 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase. Int J Pharmacol. 2010;6:705–711.
-
- Maron DJ, Fazio S, Linton MF. Current perspectives on statins. Circulation. 2000;101(2):207–213. - PubMed
-
- Loke WM, Proudfoot JM, Hodgson JM, et al. Specific dietary poly-phenols attenuate atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice by alleviating inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(4):749–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

